PLK4 as a potential target to enhance radiosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 38365710
- PMCID: PMC10873955
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-024-02410-z
PLK4 as a potential target to enhance radiosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
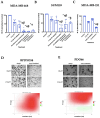
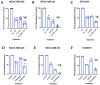
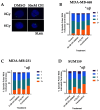
Radioresistance is one of the barriers to developing more effective therapies against the most aggressive, triple-negative, breast cancer (TNBC) subtype. In our previous studies, we showed that inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 4 (PLK4) by a novel drug, CFI-400945 significantly enhances the anticancer effects of radiotherapy (RT) compared to single treatment alone. Here we further investigate the role of PLK4 in enhancing radiation effects in TNBC and explore mechanisms of PLK4 inhibition and radiation combinatorial antiproliferative effects. To assess cellular proliferation in response to treatments, we used colony formation assays in TNBC cell lines and patient-derived organoids (PDOs). Downregulation of PLK4 expression was achieved using siRNA silencing in TNBC cell lines. Immunofluorescence against centrin was used to assess the alteration of centriole amplification in response to treatments. We observed that inhibition of PLK4 by CFI-400945 or Centrinone B or its downregulation by siRNA, when combined with RT, resulted in a significant increase in antiproliferative effect in TNBC cells lines and PDOs compared to untreated or single-treated cells. Anticancer synergy was observed using a response matrix in PDOs treated with CFI-400945 and RT. We show that the overamplification of centrioles might be involved in the combined antiproliferative action of RT and PLK4 inhibition. Our data suggest that PLK4 is a promising target for enhancing the anticancer effects of RT in TNBC that, at least in part, is modulated by the overamplification of centrioles. These results support further mechanistic and translational studies of anti-PLK4 agents and RT as an anticancer combination treatment strategy.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; CFI-400945; Centrinone B; Centrosome; Combination therapy; Organoids; PLK4; Radiotherapy; Triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.W.C. reports advisory services to AstraZeneca, Exact Sciences, Eisai, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Inivata, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; reports research funding (to institution) from AstraZeneca, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Inivata, Merck, Pfizer, and Roche; is a member of a trial steering committee for AstraZeneca, Merck, and GlaxoSmithKline; and D.W.C. holds a patent (US62/675,228) for methods of treating cancers characterized by a high expression level of spindle and kinetochore associated complex subunit 3 (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anticancer effects of radiation therapy combined with Polo-Like Kinase 4 (PLK4) inhibitor CFI-400945 in triple negative breast cancer.Breast. 2021 Aug;58:6-9. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Breast. 2021. PMID: 33866248 Free PMC article.
-
BUB1 regulates non-homologous end joining pathway to mediate radioresistance in triple-negative breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 11;43(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03086-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38863037 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Protein Kinase Inhibitors with PLK4 Cross-Over Potential in a Pre-Clinical Model of Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 29;20(9):2112. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092112. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035676 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting polo-like kinase 4.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Feb 5;265:116115. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.116115. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38199166 Review.
-
Enhancing radiotherapy techniques for Triple-Negative breast cancer treatment.Cancer Treat Rev. 2025 May;136:102939. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2025.102939. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Cancer Treat Rev. 2025. PMID: 40286498 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on factors affecting the sensitivity of breast cancer to radiotherapy: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 31;13(7):3869-3888. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-71. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39145054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosomal Instability and Clonal Heterogeneity in Breast Cancer: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 4;17(7):1222. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071222. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transformative Role of 3D Culture Models in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Research.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 13;16(10):1859. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101859. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Under Radiation Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 20;26(6):2795. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062795. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centrosomes and associated proteins in pathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 28;14:1370565. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1370565. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38606093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

