Plasma N-terminal containing tau fragments (NTA-tau): a biomarker of tau deposition in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38365825
- PMCID: PMC10874032
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-024-00707-x
Plasma N-terminal containing tau fragments (NTA-tau): a biomarker of tau deposition in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Novel phosphorylated-tau (p-tau) blood biomarkers (e.g., p-tau181, p-tau217 or p-tau231), are highly specific for Alzheimer's disease (AD), and can track amyloid-β (Aβ) and tau pathology. However, because these biomarkers are strongly associated with the emergence of Aβ pathology, it is difficult to determine the contribution of insoluble tau aggregates to the plasma p-tau signal in blood. Therefore, there remains a need for a biomarker capable of specifically tracking insoluble tau accumulation in brain.
Methods: NTA is a novel ultrasensitive assay targeting N-terminal containing tau fragments (NTA-tau) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma, which is elevated in AD. Using two well-characterized research cohorts (BioFINDER-2, n = 1,294, and BioFINDER-1, n = 932), we investigated the association between plasma NTA-tau levels and disease progression in AD, including tau accumulation, brain atrophy and cognitive decline.
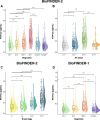
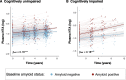
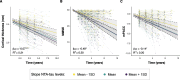
Results: We demonstrate that plasma NTA-tau increases across the AD continuum¸ especially during late stages, and displays a moderate-to-strong association with tau-PET (β = 0.54, p < 0.001) in Aβ-positive participants, while weak with Aβ-PET (β = 0.28, p < 0.001). Unlike plasma p-tau181, GFAP, NfL and t-tau, tau pathology determined with tau-PET is the most prominent contributor to NTA-tau variance (52.5% of total R2), while having very low contribution from Aβ pathology measured with CSF Aβ42/40 (4.3%). High baseline NTA-tau levels are predictive of tau-PET accumulation (R2 = 0.27), steeper atrophy (R2 ≥ 0.18) and steeper cognitive decline (R2 ≥ 0.27) in participants within the AD continuum. Plasma NTA-tau levels significantly increase over time in Aβ positive cognitively unimpaired (βstd = 0.16) and impaired (βstd = 0.18) at baseline compared to their Aβ negative counterparts. Finally, longitudinal increases in plasma NTA-tau levels were associated with steeper longitudinal decreases in cortical thickness (R2 = 0.21) and cognition (R2 = 0.20).
Conclusion: Our results indicate that plasma NTA-tau levels increase across the AD continuum, especially during mid-to-late AD stages, and it is closely associated with in vivo tau tangle deposition in AD and its downstream effects. Moreover, this novel biomarker has potential as a cost-effective and easily accessible tool for monitoring disease progression and cognitive decline in clinical settings, and as an outcome measure in clinical trials which also need to assess the downstream effects of successful Aβ removal.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; BioFINDER; Biomarkers; NTA; NTA-tau; Plasma; Tau; Tau pathology; Tau-PET.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
KB has served as a consultant and at advisory boards for Acumen, ALZPath, BioArctic, Biogen, Eisai, Julius Clinical, Lilly, Novartis, Ono Pharma, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers; has served at data monitoring committees for Julius Clinical and Novartis; has given lectures, produced educational materials and participated in educational programs for Biogen, Eisai and Roche Diagnostics; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work). OH has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer, and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Amylyx, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Cerveau, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Genentech, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi and Siemens. JLR, GS, AES, LMG, WSB, ALB, NMC, PT, SJ, SP, ES and NJA report no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022-00775/Swedish Research Council
- 2022-01018/Swedish Research Council
- 2019-02397/Swedish Research Council
- 2017-00915/Swedish Research Council
- 2022-00732/Swedish Research Council
- ERAPERMED2021-184/ERA PerMed
- 2017-0383/Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation
- AF-980907/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- AF-930351/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- AF-968270/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- FO2021-0293/Swedish Brain Foundation
- 1412/22/The Parkinson foundation of Sweden
- 2020-O000028/Skåne University Hospital Foundation
- 2022-1259/Regionalt Forskningsstöd
- 2022-Projekt0080/Swedish federal government under the ALF agreement
- 101061836/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program
- AARF-22-972612/Alzheimer's Association Research Fellowship
- 101053962/uropean Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme
- ALFGBG-71320/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- 201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF)
- ADSF-21-831376-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- ADSF-21-831381-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- ADSF-21-831377-C/AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer's Association
- FO2022-0270/Hjärnfonden
- FO2017-0243/Hjärnfonden
- ALZ2022-0006/Hjärnfonden
- 860197/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- JPND2021-00694/European Union Joint Programme - Neurodegenerative Disease Research
- UKDRI-1003/UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL
- AF-939721/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- ALFGBG-715986/Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the County Councils, the ALF-agreement
- ALFGBG-965240/Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the County Councils, the ALF-agreement
- JPND2019-466-236/European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders
- ZEN-21-848495/Alzheimer's Association 2021 Zenith Award
- SG-23-1038904 QC/Alzheimer's Association 2022-2025 Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

