Synaptotagmin-7 Counteracts Short-Term Depression during Phasic Dopamine Release
- PMID: 38365841
- PMCID: PMC10932592
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0501-23.2024
Synaptotagmin-7 Counteracts Short-Term Depression during Phasic Dopamine Release
Abstract
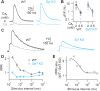
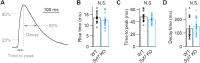
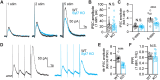
Dopamine neurons switch from tonic pacemaker activity to high-frequency bursts in response to salient stimuli. These bursts lead to superlinear increases in dopamine release, and the degree of this increase is highly dependent on firing frequency. The superlinearity and frequency dependence of dopamine release implicate short-term plasticity processes. The presynaptic Ca2+-sensor synaptotagmin-7 (SYT7) has suitable properties to mediate such short-term plasticity and has been implicated in regulating dopamine release from somatodendritic compartments. Here, we use a genetically encoded dopamine sensor and whole-cell electrophysiology in Syt7 KO mice to determine how SYT7 contributes to both axonal and somatodendritic dopamine release. We find that SYT7 mediates a hidden component of facilitation of release from dopamine terminals that can be unmasked by lowering initial release probability or by predepressing synapses with low-frequency stimulation. Depletion of SYT7 increased short-term depression and reduced release during stimulations that mimic in vivo firing. Recordings of D2-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) confirmed a similar role for SYT7 in somatodendritic release. Our results indicate that SYT7 drives short-term facilitation of dopamine release, which may explain the frequency dependence of dopamine signaling seen in vivo.
Keywords: dopamine; short-term plasticity; synaptotagmin.
Copyright © 2024 Lebowitz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
