Longitudinal gut microbiome changes in immune checkpoint blockade-treated advanced melanoma
- PMID: 38365950
- PMCID: PMC10957474
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02803-3
Longitudinal gut microbiome changes in immune checkpoint blockade-treated advanced melanoma
Abstract
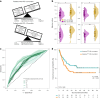
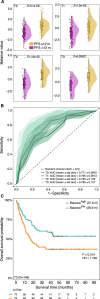
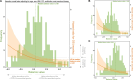
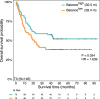
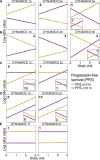
Multiple clinical trials targeting the gut microbiome are being conducted to optimize treatment outcomes for immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). To improve the success of these interventions, understanding gut microbiome changes during ICB is urgently needed. Here through longitudinal microbiome profiling of 175 patients treated with ICB for advanced melanoma, we show that several microbial species-level genome bins (SGBs) and pathways exhibit distinct patterns from baseline in patients achieving progression-free survival (PFS) of 12 months or longer (PFS ≥12) versus patients with PFS shorter than 12 months (PFS <12). Out of 99 SGBs that could discriminate between these two groups, 20 were differentially abundant only at baseline, while 42 were differentially abundant only after treatment initiation. We identify five and four SGBs that had consistently higher abundances in patients with PFS ≥12 and <12 months, respectively. Constructing a log ratio of these SGBs, we find an association with overall survival. Finally, we find different microbial dynamics in different clinical contexts including the type of ICB regimen, development of immune-related adverse events and concomitant medication use. Insights into the longitudinal dynamics of the gut microbiome in association with host factors and treatment regimens will be critical for guiding rational microbiome-targeted therapies aimed at enhancing ICB efficacy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.K.W. acted as a consultant for Takeda; received unrestricted research grants from Takeda, Johnson & Johnson, Tramedico and Ferring; and received speaker fees from MSD, AbbVie and Janssen Pharmaceuticals. E.G.E.d.V. reports an advisory role at Daiichi Sankyo, NSABP and Sanofi (paid to University Medical Center Groningen) and research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Chugai Pharma, CytomX Therapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech, Nordic Nanovector, Radius Health, Regeneron, Roche, Servier and Synthon (paid to University Medical Center Groningen). S.P. received speaker fees from Almirall, BMS, ISDIN, La Roche Posay, Leo Pharma, Regeneron, Roche and Sanofi; acted as advisory board member of Almirall, ISDIN, La Roche Posay, Pfizer, Roche, Regeneron, Sanofi and Sun Pharma; and received research funding from Abbie, AMGEN, ISDIN, La Roche Posay, Leo Pharma and Novartis. R.B. has received honoraria from, and sits on advisory boards of, Novartis, BMS and MSD. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

