Role of the histone variant H2A.Z.1 in memory, transcription, and alternative splicing is mediated by lysine modification
- PMID: 38366138
- PMCID: PMC11224360
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-024-01817-2
Role of the histone variant H2A.Z.1 in memory, transcription, and alternative splicing is mediated by lysine modification
Abstract
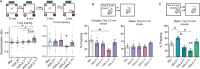
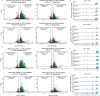
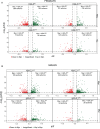
Creating long-lasting memories requires learning-induced changes in gene expression, which are impacted by epigenetic modifications of DNA and associated histone proteins. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histones are key regulators of transcription, with different PTMs producing unique effects on gene activity and behavior. Although recent studies implicate histone variants as novel regulators of memory, effects of PTMs on the function of histone variants are rarely considered. We previously showed that the histone variant H2A.Z suppresses memory, but it is unclear if this role is impacted by H2A.Z acetylation, a PTM that is typically associated with positive effects on transcription and memory. To answer this question, we used a mutation approach to manipulate acetylation on H2A.Z without impacting acetylation of other histone types. Specifically, we used adeno-associated virus (AAV) constructs to overexpress mutated H2A.Z.1 isoforms that either mimic acetylation (acetyl-mimic) by replacing lysines 4, 7 and 11 with glutamine (KQ), or H2A.Z.1 with impaired acetylation (acetyl-defective) by replacing the same lysines with alanine (KA). Expressing the H2A.Z.1 acetyl-mimic (H2A.Z.1KQ) improved memory under weak learning conditions, whereas expressing the acetyl-defective H2A.Z.1KA generally impaired memory, indicating that the effect of H2A.Z.1 on memory depends on its acetylation status. RNA sequencing showed that H2A.Z.1KQ and H2A.Z.1KA uniquely impact the expression of different classes of genes in both females and males. Specifically, H2A.Z.1KA preferentially impacts genes involved in synaptic function, suggesting that acetyl-defective H2A.Z.1 impairs memory by altering synaptic regulation. Finally, we describe, for the first time, that H2A.Z is also involved in alternative splicing of neuronal genes, whereby H2A.Z depletion, as well as expression of H2A.Z.1 lysine mutants influence transcription and splicing of different gene targets, suggesting that H2A.Z.1 can impact behavior through effects on both splicing and gene expression. This is the first study to demonstrate that direct manipulation of H2A.Z post-translational modifications regulates memory, whereby acetylation adds another regulatory layer by which histone variants can fine tune higher brain functions through effects on gene expression and splicing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35 GM137833/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RGPIN2020-06911/Canadian Network for Research and Innovation in Machining Technology, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC Canadian Network for Research and Innovation in Machining Technology)
- RGPIN-2015-05115/Gouvernement du Canada | Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Conseil de Recherches en Sciences Naturelles et en Génie du Canada)
- PJT-156414/Gouvernement du Canada | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Instituts de Recherche en Santé du Canada)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

