Ripple-locked coactivity of stimulus-specific neurons and human associative memory
- PMID: 38366143
- PMCID: PMC10917673
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01550-x
Ripple-locked coactivity of stimulus-specific neurons and human associative memory
Abstract
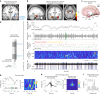
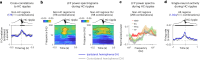
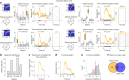
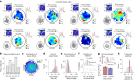
Associative memory enables the encoding and retrieval of relations between different stimuli. To better understand its neural basis, we investigated whether associative memory involves temporally correlated spiking of medial temporal lobe (MTL) neurons that exhibit stimulus-specific tuning. Using single-neuron recordings from patients with epilepsy performing an associative object-location memory task, we identified the object-specific and place-specific neurons that represented the separate elements of each memory. When patients encoded and retrieved particular memories, the relevant object-specific and place-specific neurons activated together during hippocampal ripples. This ripple-locked coactivity of stimulus-specific neurons emerged over time as the patients' associative learning progressed. Between encoding and retrieval, the ripple-locked timing of coactivity shifted, suggesting flexibility in the interaction between MTL neurons and hippocampal ripples according to behavioral demands. Our results are consistent with a cellular account of associative memory, in which hippocampal ripples coordinate the activity of specialized cellular populations to facilitate links between stimuli.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patterns of single-neuron activity during associative recognition memory in the human medial temporal lobe.Neuroimage. 2020 Nov 1;221:117214. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117214. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32755669
-
Neurons in the human medial temporal lobe track multiple temporal contexts during episodic memory processing.Neuroimage. 2021 Dec 15;245:118689. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118689. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34742943 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal ripples signal contextually mediated episodic recall.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 4;119(40):e2201657119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201657119. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36161912 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of rhinal cortex and hippocampus in human declarative memory formation.Rev Neurosci. 2002;13(4):299-312. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2002.13.4.299. Rev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12542259 Review.
-
Neuronal ensemble dynamics in associative learning.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;73:102530. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102530. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35367858 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane potential states gate synaptic consolidation in human neocortical tissue.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 12;15(1):10340. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53901-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39668146 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal and cortical high-frequency oscillations orchestrate human semantic networks during word list memory.iScience. 2025 Mar 13;28(4):112171. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112171. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40235588 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiological evidence of human hippocampal longitudinal differentiation in associative memory.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 25;16(1):6845. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61464-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40715077 Free PMC article.
-
Theta-phase locking of single neurons during human spatial memory.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 20:2024.06.20.599841. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.20.599841. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 11;16(1):7402. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62553-9. PMID: 38948829 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Movie-watching evokes ripple-like activity within events and at event boundaries.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5647. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60788-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahana, M. J. Foundations of Human Memory (Oxford Univ. Press, 2014).
-
- Naveh-Benjamin M. Adult age differences in memory performance: tests of an associative deficit hypothesis. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2000;26:1170–1187. - PubMed
-
- Squire LR, Stark CEL, Clark RE. The medial temporal lobe. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004;27:279–306. - PubMed
-
- Neves G, Cooke SF, Bliss TVP. Synaptic plasticity, memory and the hippocampus: a neural network approach to causality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008;9:65–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

