CRISPR-targeted mutagenesis of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 improves both immunity and yield in wheat
- PMID: 38366355
- PMCID: PMC11182583
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.14312
CRISPR-targeted mutagenesis of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 improves both immunity and yield in wheat
Abstract
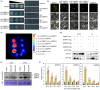
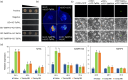
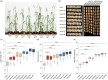
Plants have evolved a sophisticated immunity system for specific detection of pathogens and rapid induction of measured defences. Over- or constitutive activation of defences would negatively affect plant growth and development. Hence, the plant immune system is under tight positive and negative regulation. MAP kinase phosphatase1 (MKP1) has been identified as a negative regulator of plant immunity in model plant Arabidopsis. However, the molecular mechanisms by which MKP1 regulates immune signalling in wheat (Triticum aestivum) are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the role of TaMKP1 in wheat defence against two devastating fungal pathogens and determined its subcellular localization. We demonstrated that knock-down of TaMKP1 by CRISPR/Cas9 in wheat resulted in enhanced resistance to rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst) and powdery mildew caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici (Bgt), indicating that TaMKP1 negatively regulates disease resistance in wheat. Unexpectedly, while Tamkp1 mutant plants showed increased resistance to the two tested fungal pathogens they also had higher yield compared with wild-type control plants without infection. Our results suggested that TaMKP1 interacts directly with dephosphorylated and activated TaMPK3/4/6, and TaMPK4 interacts directly with TaPAL. Taken together, we demonstrated TaMKP1 exert negative modulating roles in the activation of TaMPK3/4/6, which are required for MAPK-mediated defence signalling. This facilitates our understanding of the important roles of MAP kinase phosphatases and MAPK cascades in plant immunity and production, and provides germplasm resources for breeding for high resistance and high yield.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; MAP kinase phosphatase 1; MPK3; MPK4; MPK6; wheat defence responses.
© 2024 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Simultaneous modification of three homoeologs of TaEDR1 by genome editing enhances powdery mildew resistance in wheat.Plant J. 2017 Aug;91(4):714-724. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13599. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28502081
-
Wheat WD40-repeat protein TaHOS15 functions in a histone deacetylase complex to fine-tune defense responses to Blumeria graminis f.sp. tritici.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jan 1;70(1):255-268. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery330. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30204899
-
The NB-LRR gene Pm60 confers powdery mildew resistance in wheat.New Phytol. 2018 Apr;218(1):298-309. doi: 10.1111/nph.14964. Epub 2017 Dec 27. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 29281751
-
Transcriptome analysis of genes related to resistance against powdery mildew in wheat-Thinopyrum alien addition disomic line germplasm SN6306.Gene. 2016 Sep 15;590(1):5-17. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27265028 Review.
-
Proteolysis in plant immunity.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3099-3115. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae142. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38723588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR-mediated genome editing of wheat for enhancing disease resistance.Front Genome Ed. 2025 Feb 25;7:1542487. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2025.1542487. eCollection 2025. Front Genome Ed. 2025. PMID: 40070798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9: a sustainable technology to enhance climate resilience in major Staple Crops.Front Genome Ed. 2025 Mar 18;7:1533197. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2025.1533197. eCollection 2025. Front Genome Ed. 2025. PMID: 40171546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of CRISPR Technology in Gene Editing for Tolerance to Biotic Factors in Plants: A Systematic Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 2;46(10):11086-11123. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100659. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 controls broad spectrum disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana through diverse mechanisms of immune activation.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 21;15:1374194. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1374194. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38576784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, J.C. , Bartels, S. , Besteiro, M.A.G. , Shahollari, B. , Ulm, R. and Peck, S.C. (2011) Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) negatively regulates MPK6‐mediated PAMP responses and resistance against bacteria. Plant J. 67, 258–268. - PubMed
-
- Bartels, S. , Anderson, J.C. , Gonzalez Besteiro, M.A. , Carreri, A. , Hirt, H. , Buchala, A. , Metraux, J.P. et al. (2009) MAP kinase phosphatase1 and protein tyrosine phosphatase1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and SNC1‐mediated responses in Arabidopsis . Plant Cell, 21, 2884–2897. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, J. , Wang, L.H. , Yang, Z.Y. , Liu, H.B. , Chu, C.L. , Zhang, Z.Z. , Zhang, Q.L. et al. (2021) The rice Raf‐like MAPKKK OsILA1 confers broad‐spectrum resistance to bacterial blight by suppressing the OsMAPKK4‐OsMAPK6 cascade. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 63, 1815–1832. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y.M. , Guo, Y.W. , Guan, P.F. , Wang, Y.F. , Wang, X.B. , Wang, Z.H. , Qin, Z. et al. (2023) A wheat integrative regulatory network from large‐ scale complementary functional datasets enables trait‐associated gene discovery for crop improvement. Mol. Plant 16, 393–414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

