High fat intake sustains sorbitol intolerance after antibiotic-mediated Clostridia depletion from the gut microbiota
- PMID: 38366592
- PMCID: PMC11023689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.029
High fat intake sustains sorbitol intolerance after antibiotic-mediated Clostridia depletion from the gut microbiota
Abstract
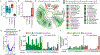
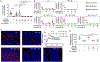
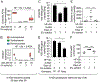
Carbohydrate intolerance, commonly linked to the consumption of lactose, fructose, or sorbitol, affects up to 30% of the population in high-income countries. Although sorbitol intolerance is attributed to malabsorption, the underlying mechanism remains unresolved. Here, we show that a history of antibiotic exposure combined with high fat intake triggered long-lasting sorbitol intolerance in mice by reducing Clostridia abundance, which impaired microbial sorbitol catabolism. The restoration of sorbitol catabolism by inoculation with probiotic Escherichia coli protected mice against sorbitol intolerance but did not restore Clostridia abundance. Inoculation with the butyrate producer Anaerostipes caccae restored a normal Clostridia abundance, which protected mice against sorbitol-induced diarrhea even when the probiotic was cleared. Butyrate restored Clostridia abundance by stimulating epithelial peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ) signaling to restore epithelial hypoxia in the colon. Collectively, these mechanistic insights identify microbial sorbitol catabolism as a potential target for approaches for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of sorbitol intolerance.
Keywords: Clostridia; antibiotics; carbohydrate intolerance; gut microbiota; high-fat diet; polyol; sorbitol intolerance.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK114034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI112949/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AT011117/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044170/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI146432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI096528/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112949/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK098722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI153069/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122593/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112445/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010786/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR074500/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

