Conditioned Medium From Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Alleviates Mouse Osteoarthritis by Inducing sFRP1-Expressing M2 Macrophages
- PMID: 38366885
- PMCID: PMC11016837
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szae006
Conditioned Medium From Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Alleviates Mouse Osteoarthritis by Inducing sFRP1-Expressing M2 Macrophages
Abstract
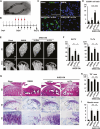
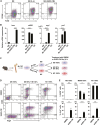
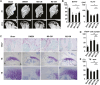
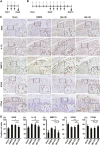
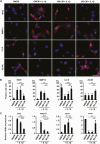
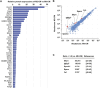
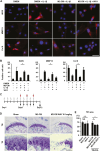
Intravenous administration of conditioned medium from stem cells of human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED-CM) regenerates mechanically injured osteochondral tissues in mouse temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJOA). However, the underlying therapeutic mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we showed that SHED-CM alleviated injured TMJ by inducing anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages in the synovium. Depletion of M2 by Mannosylated Clodrosome abolished the osteochondral repair activities of SHED-CM. Administration of CM from M2-induced by SHED-CM (M2-CM) effectively ameliorated mouse TMJOA by inhibiting chondrocyte inflammation and matrix degradation while enhancing chondrocyte proliferation and matrix formation. Notably, in vitro, M2-CM directly suppressed the catabolic activities while enhancing the anabolic activities of interleukin-1β-stimulated mouse primary chondrocytes. M2-CM also inhibited receptor activator of nuclear factor NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells. Secretome analysis of M2-CM and M0-CM revealed that 5 proteins related to anti-inflammation and/or osteochondrogenesis were enriched in M2-CM. Of these proteins, the Wnt signal antagonist, secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (sFRP1), was the most abundant and played an essential role in the shift to anabolic chondrocytes, suggesting that M2 ameliorated TMJOA partly through sFRP1. This study suggests that secretome from SHED exerted remarkable osteochondral regeneration activities in TMJOA through the induction of sFRP1-expressing tissue-repair M2 macrophages.
Keywords: Wnt antagonist; dental pulp stem cell; mesenchymal stem cell; osteoarthritis; osteochondral regeneration; secretome of M2 macrophage; temporomandibular joint.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
A.Y. is a funding scientist and a paid scientific advisory board member of SHED Tech Corporation. All the other authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020 Jun;28(6):831-841. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.03.010. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020. PMID: 32272195
-
Protective effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth derived conditioned medium on osteoarthritic chondrocytes.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 4;15(9):e0238449. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238449. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32886713 Free PMC article.
-
Factors secreted from the stem cells of human exfoliated deciduous teeth inhibit osteoclastogenesis through the activation of the endogenous antioxidant system.J Oral Biosci. 2025 Mar;67(1):100618. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2025.100618. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Oral Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39855425
-
From Teeth to Therapy: A Review of Therapeutic Potential within the Secretome of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11763. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth and their Derivatives in Inflammatory Diseases Therapy.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(4):302-316. doi: 10.2174/1574888X17666220417153309. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35440314 Review.
Cited by
-
Small extracellular vesicles derived from auricular chondrocytes promote secretion of interleukin 10 in bone marrow M1-like macrophages.Regen Ther. 2025 Jan 24;28:421-430. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.01.009. eCollection 2025 Mar. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 39925964 Free PMC article.
-
DPSCs modulate synovial macrophage polarization and efferocytosis via PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 9;16(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04468-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40629418 Free PMC article.
-
S-propargyl-cysteine attenuates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by regulating macrophage polarization via Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling.Mol Med. 2025 Apr 7;31(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01186-6. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40197110 Free PMC article.
-
SHED-derived exosome-mimetics promotes rotator cuff tendon-bone healing via macrophage immunomodulation through NF-κB suppression and autophagy activation.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 28;34:102146. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102146. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40809349 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles from adipose-derived stromal/stem cells reprogram dendritic cells to alleviate rat TMJOA by transferring mitochondria.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 28;23(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03478-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40426246 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

