A Phase I Dose-Escalation Clinical Trial to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38366909
- PMCID: PMC10940813
- DOI: 10.1093/stcltm/szad088
A Phase I Dose-Escalation Clinical Trial to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
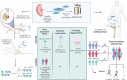
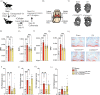
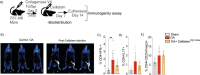
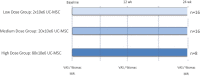
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common degenerative joint disease. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) are promising cell-based therapy for OA. However, there is still a need for additional randomized, dose-dependent studies to determine the optimal dose and tissue source of MSC for improved clinical outcomes. Here, we performed a dose-dependant evaluation of umbilical cord (UC)-derived MSC (Celllistem) in a murine model and in knee OA patients. For the preclinical study, a classical dose (200.000 cells) and a lower dose (50.000 cells) of Cellistem were intra-articularly injected into the mice knee joints. The results showed a dose efficacy response effect of Cellistem associated with a decreased inflammatory and degenerative response according to the Pritzker OARSI score. Following the same approach, the dose-escalation phase I clinical trial design included 3 sequential cohorts: low-dose group (2 × 106 cells), medium-dose group (20 × 106), and high-dose group (80 × 106). All the doses were safe, and no serious adverse events were reported. Nonetheless, 100% of the patients injected with the high-dose experienced injection-related swelling in the knee joint. According to WOMAC total outcomes, patients treated with all doses reported significant improvements in pain and function compared with baseline after 3 and 6 months. However, the improvements were higher in patients treated with both medium and low dose as compared to high dose. Therefore, our data demonstrate that the intra-articular injection of different doses of Cellistem is both safe and efficient, making it an interesting therapeutic alternative to treat mild and symptomatic knee OA patients. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03810521.
Keywords: dose escalation; murine OA model; osteoarthritis; phase I clinical trial; umbilical-cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Maroun Khoury reports receiving grants from ANID, during the conduct of the study and other from Cells for Cells. In addition, Dr. Khoury is the inventor of patents related to mesenchymal stem cells including a patent WO2014135924A1 pending, a patent WO2017064670A2 pending, a patent WO2017064672A1 pending, and a patent WO/2019/051623 pending.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) for Knee Osteoarthritis: Repeated MSC Dosing Is Superior to a Single MSC Dose and to Hyaluronic Acid in a Controlled Randomized Phase I/II Trial.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Mar;8(3):215-224. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0053. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30592390 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy for Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Phase I Dose-Escalation Trial.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):847-56. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0245. Epub 2016 May 23. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27217345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Efficacy of Intra-articular Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blinded Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Mar;48(3):588-598. doi: 10.1177/0363546519899923. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 32109160 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra-Articular Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Injections Are No Different From Placebo in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Arthroscopy. 2021 Jan;37(1):340-358. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2020.10.016. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Arthroscopy. 2021. PMID: 33098949
-
Intra-articular Injection of Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cells or Stromal Vascular Fractions: Are They Effective for Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis? A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2023 Mar;51(3):837-848. doi: 10.1177/03635465211053893. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Am J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 35019764
Cited by
-
Reconstitution of T cell-mediated immunity by umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in ulcerative colitis.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70452. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70452. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40842289 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein Activation by Retinoic Acid-Inducible Gene I Agonist Triggers Potent Antiviral Defense in Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Without Compromising Mitochondrial Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 14;26(10):4686. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104686. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429828 Free PMC article.
-
Subchondral injection of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoblast apoptosis and TGF-beta activity.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 9;16(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04366-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40346614 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Cellular Dosage of Bone Marrow Aspiration Concentrate Does Not Translate to Increased Clinical Effectiveness in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Phase I Dose Escalation Study.Indian J Orthop. 2024 Jun 5;58(8):1001-1008. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01197-1. eCollection 2024 Aug. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39087042 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell exosome therapy: current research status in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and the possibility of reversing normal brain aging.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Feb 21;16(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04160-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39985030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han S. Osteoarthritis year in review 2022: Biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(12):1575-1582. - PubMed
-
- Gupta PK, Chullikana A, Rengasamy M, et al. . Efficacy and safety of adult human bone marrow-derived, cultured, pooled, allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells (Stempeucel®): preclinical and clinical trial in osteoarthritis of the knee joint. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):301. 10.1186/s13075-016-1195-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

