In vivo study to assess fat embolism resulting from the Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator 2 system compared to a novel aspirator-based concept for intramedullary bone graft harvesting
- PMID: 38367064
- PMCID: PMC10965743
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-024-05220-w
In vivo study to assess fat embolism resulting from the Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator 2 system compared to a novel aspirator-based concept for intramedullary bone graft harvesting
Abstract
Introduction: Fat embolism (FE) following intramedullary (IM) reaming can cause severe pulmonary complications and sudden death. Recently, a new harvesting concept was introduced in which a novel aspirator is used first for bone marrow (BM) aspiration and then for subsequent aspiration of morselized endosteal bone during sequential reaming (A + R + A). In contrast to the established Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator (RIA) 2 system, the new A + R + A concept allows for the evacuation of fatty BM prior to reaming. In this study, we hypothesized that the risk of FE, associated coagulopathic reactions and pulmonary FE would be comparable between the RIA 2 system and the A + R + A concept.
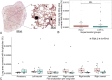
Materials and methods: Intramedullary bone graft was harvested from intact femora of 16 Merino sheep (age: 1-2 years) with either the RIA 2 system (n = 8) or the A + R + A concept (n = 8). Fat intravasation was monitored with the Gurd test, coagulopathic response with D-dimer blood level concentration and pulmonary FE with histological evaluation of the lungs.
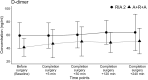
Results: The total number and average size of intravasated fat particles was similar between groups (p = 0.13 and p = 0.98, respectively). D-dimer concentration did not significantly increase within 4 h after completion of surgery (RIA 2: p = 0.82; A + R + A: p = 0.23), with an interaction effect similar between groups (p = 0.65). The average lung area covered with fat globules was similar between groups (p = 0.17).
Conclusions: The use of the RIA 2 system and the novel A + R + A harvesting concept which consists of BM evacuation followed by sequential IM reaming and aspiration of endosteal bone, resulted in only minor fat intravasation, coagulopathic reactions and pulmonary FE, with no significant differences between the groups. Our results, therefore, suggest that both the RIA 2 system and the new A + R + A concept are comparable technologies in terms of FE-related complications.
Keywords: Bone graft; Fat embolism; Harvesting; Reaming.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
FH received consulting fees from Stryker. All other authors declare that the research leading to this study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator System: A Review.Surg Technol Int. 2016 Oct 26;29:287-294. Surg Technol Int. 2016. PMID: 27728952 Review.
-
An in vivo study to investigate an original intramedullary bone graft harvesting technology.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Sep 15;28(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01328-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37715198 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical techniques: how I do it? The Reamer/Irrigator/Aspirator (RIA) system.Injury. 2009 Nov;40(11):1231-6. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.07.070. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Injury. 2009. PMID: 19783249
-
Harvest of cortico-cancellous intramedullary femoral bone graft using the Reamer-Irrigator-Aspirator (RIA).Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012 Apr;98(2):227-32. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.01.003. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012. PMID: 22402294
-
Reamer-irrigator-aspirator indications and clinical results: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2011 Jul;35(7):951-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-010-1189-z. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Int Orthop. 2011. PMID: 21243358 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessing Cardiopulmonary Safety of Intramedullary Bone Graft Harvesting: A Comparative Study of the RIA 2 System and the ARA Concept.J Orthop Res. 2025 May;43(5):984-993. doi: 10.1002/jor.26059. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Orthop Res. 2025. PMID: 40001236 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

