Selection of epigenetically privileged HIV-1 proviruses during treatment with panobinostat and interferon-α2a
- PMID: 38367616
- PMCID: PMC10903630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.037
Selection of epigenetically privileged HIV-1 proviruses during treatment with panobinostat and interferon-α2a
Abstract
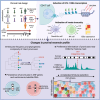
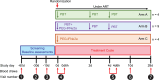
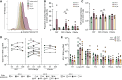
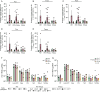
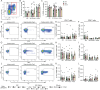
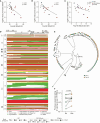
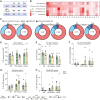
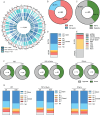
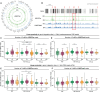
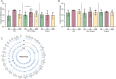
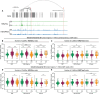
CD4+ T cells with latent HIV-1 infection persist despite treatment with antiretroviral agents and represent the main barrier to a cure of HIV-1 infection. Pharmacological disruption of viral latency may expose HIV-1-infected cells to host immune activity, but the clinical efficacy of latency-reversing agents for reducing HIV-1 persistence remains to be proven. Here, we show in a randomized-controlled human clinical trial that the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat, when administered in combination with pegylated interferon-α2a, induces a structural transformation of the HIV-1 reservoir cell pool, characterized by a disproportionate overrepresentation of HIV-1 proviruses integrated in ZNF genes and in chromatin regions with reduced H3K27ac marks, the molecular target sites for panobinostat. By contrast, proviruses near H3K27ac marks were actively selected against, likely due to increased susceptibility to panobinostat. These data suggest that latency-reversing treatment can increase the immunological vulnerability of HIV-1 reservoir cells and accelerate the selection of epigenetically privileged HIV-1 proviruses.
Keywords: HIV-1; HIV-1 cure; epigenetics; histone acetylation; innate immunity; integration sites; interferon; panobinostat; shock and kill; viral reservoir.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests D.R.K. discloses having received research funding and a speaker fee from Novartis.
Figures


References
-
- Finzi D., Hermankova M., Pierson T., Carruth L.M., Buck C., Chaisson R.E., Quinn T.C., Chadwick K., Margolick J., Brookmeyer R., et al. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science. 1997;278:1295–1300. - PubMed
-
- Wong J.K., Hezareh M., Günthard H.F., Havlir D.V., Ignacio C.C., Spina C.A., Richman D.D. Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science. 1997;278:1291–1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI184094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI174998/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI155233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA241762/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL160748/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164562/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142791/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI135940/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI155171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI125051/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DA047034/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI152979/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI149680/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R61 DA047034/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI176579/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI117841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164560/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164566/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

