Validation of a mouse 3D gastruloid-based embryotoxicity assay in reference to the ICH S5(R3) guideline chemical exposure list
- PMID: 38367697
- PMCID: PMC11016378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2024.108558
Validation of a mouse 3D gastruloid-based embryotoxicity assay in reference to the ICH S5(R3) guideline chemical exposure list
Abstract
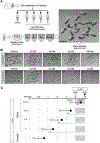
There is growing interest in establishing alternative methods in place of conventional animal tests to assess the developmental and reproductive toxicity (DART) of chemicals. Gastruloids are 3D aggregates of pluripotent stem cells that spontaneously exhibit axial elongation morphogenesis similar to gastrulation. They have been explored as in vitro embryogenesis models for developmental and toxicological studies. Here, a mouse gastruloid-based assay was validated for DART assessment in accordance with the ICH S5(R3) guideline, which provides the plasma concentration data of various reference drugs in rodents, specifically Cmax and AUC for NOAEL and LOAEL. First, adverse effect concentrations of the reference drugs and their known metabolites on gastruloid development were determined based on morphological impact, namely reduced growth or aberrant elongation. Then, the NOAEL to LOAEL concentration range obtained from the gastruloid assay was compared with that in rodents to examine similarities in sensitivity between the in vitro and in vivo assays for each chemical. For 18 out of the 24 reference drugs that have both NOAEL and LOAEL information in rodents, the sensitivity of the gastruloid assay was comparable to the in vivo assay within an 8-fold concentration margin. For 7 out of the 8 additional reference drugs that have only NOAEL or LOAEL information in rodents, the gastruloid assay was in line with the in vivo data. Altogether, these results support the effectiveness of the gastruloid assay, which may be exploited as a non-animal alternative method for DART assessment.
Keywords: Embryotoxicity; Gastruloid; ICH S5(R3) guideline; New approach methodology (NAM); P19C5; Pluripotent stem cell.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

