Ultrahigh frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for neuropathic pain alleviation and neuromodulation
- PMID: 38368171
- PMCID: PMC10943071
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00336
Ultrahigh frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for neuropathic pain alleviation and neuromodulation
Abstract
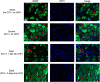
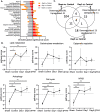
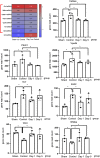
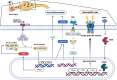
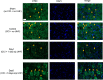
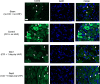
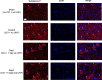
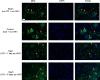
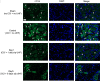
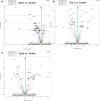
A challenging complication in patients with peripheral compressive neuropathy is neuropathic pain. Excessive neuroinflammation at the injury site worsens neuropathic pain and impairs function. Currently, non-invasive modulation techniques like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) have shown therapeutic promise with positive results. However, the underlying regulatory molecular mechanism for pain relief remains complex and unexplored. This study aimed to validate the therapeutic effect of ultrahigh frequency (UHF)-TENS in chronic constriction injury of the rat sciatic nerve. Alleviation of mechanical allodynia was achieved through the application of UHF-TENS, lasting for 3 days after one session of therapy and 4 days after two sessions, without causing additional damage to the myelinated axon structure. The entire tissue collection schedule was divided into four time points: nerve exposure surgery, 7 days after nerve ligation, and 1 and 5 days after one session of UHF therapy. Significant reductions in pain-related neuropeptides, MEK, c-Myc, c-FOS, COX2, and substance P, were observed in the injured DRG neurons after UHF therapy. RNA sequencing of differential gene expression in sensory neurons revealed significant downregulation in Cables, Pik3r1, Vps4b, Tlr7, and Ezh2 after UHF therapy, while upregulation was observed in Nfkbie and Cln3. UHF-TENS effectively and safely relieved neuropathic pain without causing further nerve damage. The decreased production of pain-related neuropeptides within the DRG provided the therapeutic benefit. Possible molecular mechanisms behind UHF-TENS may result from the modulation of the NF-κB complex, toll-like receptor-7, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. These results suggest the neuromodulatory effects of UHF-TENS in rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury, including alleviation of neuropathic pain, amelioration of pain-related neuropeptides, and regulation of neuroinflammatory gene expression. In combination with the regulation of related neuroinflammatory genes, UHF-TENS could become a new modality for enhancing the treatment of neuropathic pain in the future.
Keywords: Compression neuropathy; Neuroinflammation; Neuropathic pain; Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation; Ultrahigh frequency.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Yuan-Yu Hsueh reports financial support was provided by National Science and Technology Council. Szu-Han Chen reports financial support was provided by National Science and Technology Council. Wei-Tso Lin reports a relationship with Gimer Medical Co., Ltd, New Taipei City, Taiwan that includes: employment. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Bouhassira D. Neuropathic pain: definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2019;175(1-2):16–25. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D., Lantéri-Minet M., Attal N., Laurent B., Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008;136(3):380–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

