Identification of factors affecting student academic burnout in online education during the COVID-19 pandemic using grey Delphi and grey-DEMATEL techniques
- PMID: 38368462
- PMCID: PMC10874453
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-53233-7
Identification of factors affecting student academic burnout in online education during the COVID-19 pandemic using grey Delphi and grey-DEMATEL techniques
Abstract
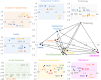
The coronavirus outbreak caused most education institutions to shift to online education. One of the consequences of the pandemic and spread of online education was the prevalence of academic burnout among students has been students' academic burnout. Accordingly, it is necessary to identify the influential factors to reduce burnout. This study aimed to identify the factors affecting academic burnout and their cause-effect relationships. For this purpose, to conduct the gray Delphi technique, a questionnaire was administered to a randomly selected sample consisted of 86 graduate students of the Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch. In addition, a randomly selected sample of 37 graduate students filled a matrix questionnaire Collected data were analyzed using the Gray-DEMATEL technique. As a result of Gray Delphi screening, out of the 43 sub-factors identified, six sub-factors were eliminated and 37 sub-factors in 7 main factors were determined as factors affecting students' academic burnout. Analysis of the collected data using the Grey-DEMATEL technique revealed that among the seven main factors, Technology infrastructure, institutional facilities, and faculty characteristics are in the net cause category, respectively. The classroom environment and course structure, the social-emotional factor, the characteristics of students, and the home and family environment are in the net effect category. Technology infrastructure is the most influential factor that affects other factors. Identifying effective factors and the causal relationships between them have significant implications for policymakers and academic planners to prevent and reduce student burnout in online environment by focusing on the most influential factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of social support and stress on academic burnout among medical students in online learning: The mediating role of resilience.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 22;10:938132. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.938132. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35937240 Free PMC article.
-
Academic Burnout, Family Functionality, Perceived Social Support and Coping among Graduate Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Mar 9;20(6):4832. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20064832. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36981741 Free PMC article.
-
Achievement Emotions of Medical Students: Do They Predict Self-regulated Learning and Burnout in an Online Learning Environment?Med Educ Online. 2023 Dec;28(1):2226888. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2023.2226888. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Med Educ Online. 2023. PMID: 38010525 Free PMC article.
-
Online medical education in Egypt during the COVID-19 pandemic: a nationwide assessment of medical students' usage and perceptions.BMC Med Educ. 2022 Mar 30;22(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03249-2. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35354406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of distance education interventions and related outcomes in primary school children during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 13;18(10):e0286674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286674. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37831672 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The influences of physical exercise on student burnout: based on the mediating role of psychological resilience.BMC Psychol. 2025 Feb 11;13(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02394-9. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39934909 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of learner background variables on academic burnout in online vs. face-to-face classes among students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences having English courses.Front Psychol. 2025 May 8;16:1484760. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1484760. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40406618 Free PMC article.
-
Fuzzy APPSS: A novel method for quantifying COVID-19 impact in India under triangular spherical fuzzy environment.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30961. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82046-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maslach C, Jackson SE. The measurement of experienced burnout. J. Occup. Behav. 1981;2(2):99–113. doi: 10.1002/job.4030020205. - DOI
-
- Schaufeli WB, Martez IM, Marques-Pinto A, Salanova M, Bakker AB. Burnout and engagement in university students: A cross-national study. J. Cross Cult. Psychol. 2002;33:464–548. doi: 10.1177/0022022102033005003. - DOI
-
- Bresó E, Salanova M, Schaufeli W. In search of the “Third Dimension” of burnout: Efficacy or inefficacy? Appl. Psychol. 2007;56:460–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-0597.2007.00290.x. - DOI
-
- Maslach C, Leiter MP. Burnout. In: Fink G, editor. Stress: Concepts, Cognition, Emotion, and Behavior. Elsevier Academic Press; 2016. pp. 351–357.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials