LC-derived excitatory synaptic transmission to dorsal raphe serotonin neurons is inhibited by activation of alpha2-adrenergic receptors
- PMID: 38368493
- PMCID: PMC11039657
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-024-01824-3
LC-derived excitatory synaptic transmission to dorsal raphe serotonin neurons is inhibited by activation of alpha2-adrenergic receptors
Abstract
In the central nervous system, noradrenaline transmission controls the degree to which we are awake, alert, and attentive. Aberrant noradrenaline transmission is associated with pathological forms of hyper- and hypo-arousal that present in numerous neuropsychiatric disorders often associated with dysfunction in serotonin transmission. In vivo, noradrenaline regulates the release of serotonin because noradrenergic input drives the serotonin neurons to fire action potentials via activation of excitatory α1-adrenergic receptors (α1-AR). Despite the critical influence of noradrenaline on the activity of dorsal raphe serotonin neurons, the source of noradrenergic afferents has not been resolved and the presynaptic mechanisms that regulate noradrenaline-dependent synaptic transmission have not been described. Using an acute brain slice preparation from male and female mice and electrophysiological recordings from dorsal raphe serotonin neurons, we found that selective optogenetic activation of locus coeruleus terminals in the dorsal raphe was sufficient to produce an α1-AR-mediated excitatory postsynaptic current (α1-AR-EPSC). Activation of inhibitory α2-adrenergic receptors (α2-AR) with UK-14,304 eliminated the α1-AR-EPSC via presynaptic inhibition of noradrenaline release, likely via inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels. In a subset of serotonin neurons, activation of postsynaptic α2-AR produced an outward current through activation of GIRK potassium conductance. Further, in vivo activation of α2-AR by systemic administration of clonidine reduced the expression of c-fos in the dorsal raphe serotonin neurons, indicating reduced neural activity. Thus, α2-AR are critical regulators of serotonin neuron excitability.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to American College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
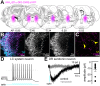

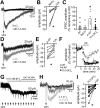
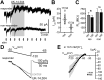
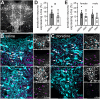
Similar articles
-
Spatiotemporal Control of Noradrenaline-Dependent Synaptic Transmission in Mouse Dorsal Raphe Serotonin Neurons.J Neurosci. 2022 Feb 9;42(6):968-979. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1176-21.2021. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34921047 Free PMC article.
-
Delta glutamate receptor conductance drives excitation of mouse dorsal raphe neurons.Elife. 2020 Apr 1;9:e56054. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56054. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32234214 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stress impairs α1-adrenoceptor-induced endocannabinoid-dependent synaptic plasticity in the dorsal raphe nucleus.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 29;34(44):14560-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1310-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25355210 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Adrenoceptors.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:185-245. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_714. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38755350 Review.
-
[Role of Median Raphe Serotonergic Neurons in Positive and Negative Information Processing].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2025;145(2):79-84. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.24-00150. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2025. PMID: 39894484 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Gene Expression Analysis Using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Derived from Patients with Sleep Bruxism: A Preliminary In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 6;25(23):13141. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313141. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684851 Free PMC article.
-
The Addition of Intrathecal Clonidine to Reduce Medication-Related Side-Effects in Cancer Pain: A Retrospective Cohort Study.J Pain Res. 2025 Mar 21;18:1503-1509. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S504556. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40176786 Free PMC article.
-
The Locus Coeruleus in Chronic Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8636. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168636. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcortical nuclei of the human ascending arousal system encode anticipated reward but do not predict subsequent memory.Cereb Cortex. 2025 May 1;35(5):bhaf101. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaf101. Cereb Cortex. 2025. PMID: 40346825 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aston-Jones G, Rajkowski J, Cohen J. Role of locus coeruleus in attention and behavioral flexibility. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46:1309–20. - PubMed
-
- Agren H, Koulu M, Saavedra JM, Potter WZ, Linnoila M. Circadian covariation of norepinephrine and serotonin in the locus coeruleus and dorsal raphe nucleus in the rat. Brain Res. 1986;397:353–8. - PubMed
-
- Baraban JM, Wang RY, Aghajanian G. Reserpine suppression of dorsal raphe neuronal firing: mediation by adrenergic system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978;52:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK. Suppression of serotonergic neuronal firing by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists: evidence against GABA mediation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980;66:287–94. - PubMed
-
- Baraban JM, Aghajanian GK. Suppression of firing activity of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe by alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology. 1980;19:355–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

