Retromer-dependent lysosomal stress in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 38368937
- PMCID: PMC10874697
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0376
Retromer-dependent lysosomal stress in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
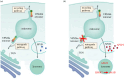
While causative mutations in complex disorders are rare, they can be used to extract a biological pathway whose pathogenicity can generalize to common forms of the disease. Here we begin by relying on the biological consequences of mutations in LRRK2 and VPS35, genetic causes of autosomal-dominant Parkinson's disease, to hypothesize that 'Retromer-dependent lysosomal stress' represents a pathway that can generalize to idiopathic Parkinson's disease. Next, we outline a series of studies that can test this hypothesis, including the development of biomarkers of pathway dysfunction. If validated, the hypothesis can suggest a unified mechanism of disease and might inform future diagnostic and therapeutic investigations. This article is part of a discussion meeting issue 'Understanding the endo-lysosomal network in neurodegeneration'.
Keywords: LRRK2; Parkinson's disease; VPS35; retromer.
Conflict of interest statement
Scott A. Small is a co-founder of Retromer Therapeutics Inc. Kalpana Merchant is the Chief Scientific Officer of Retromer Therapeutics Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

