Motor abilities in adults born with very low birthweight: A study of two birth cohorts from Finland and Norway
- PMID: 38369576
- PMCID: PMC11579805
- DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.15883
Motor abilities in adults born with very low birthweight: A study of two birth cohorts from Finland and Norway
Abstract
Aim: To compare overall, fine, and gross motor abilities in adults born preterm with very low birthweight (VLBW) and a control group of term-born individuals.
Method: In a joint assessment of the Helsinki Study of Very Low Birth Weight Adults and NTNU Low Birth Weight in a Lifetime Perspective study, data were collected with harmonized methods for 118 adults born preterm (gestational age < 37 weeks) with VLBW (≤1500 g) and 147 control individuals. The primary outcome was overall motor abilities; secondary outcomes were fine and gross motor abilities.
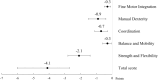
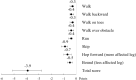
Results: The Bruininks Motor Ability Test Short Form total score was 4.1 (95% confidence interval 2.7-6.0) points lower in adults born with VLBW than in the control group, adjusted for cohort, age, and sex. This was partly mediated by their shorter height. They also had lower scores for other fine and gross motor tests. Results were similar when participants with neurosensory impairment were excluded, and when we adjusted for additional covariates.
Interpretation: Adults born preterm with VLBW had poorer overall, fine, and gross motor abilities than adults born at term. This indicates that substantial difficulties in motor function among individuals born preterm with VLBW persist into mid-adulthood.
© 2024 The Authors. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Mac Keith Press.
Figures
References
-
- Evensen KAI, Ustad T, Tikanmäki M, Haaramo P, Kajantie E. Long‐term motor outcomes of very preterm and/or very low birth weight individuals without cerebral palsy: A review of the current evidence. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2020; 25: 101116. - PubMed
-
- Edwards J, Berube M, Erlandson K, Haug S, Johnstone H, Meagher M, Sarkodee‐Adoo S, Zwicker JG. Developmental coordination disorder in school‐aged children born very preterm and/or at very low birth weight: a systematic review. J Dev Behav Pediatr 2011; 32: 678–87. - PubMed
-
- de Kieviet JF, Piek JP, Aarnoudse‐Moens CS, Oosterlaan J. Motor development in very preterm and very low‐birth‐weight children from birth to adolescence: a meta‐analysis. JAMA. 2009; 302: 2235–42. - PubMed
-
- Poole KL, Schmidt LA, Missiuna C, Saigal S, Boyle MH, Van Lieshout RJ. Childhood motor coordination and adult psychopathology in extremely low birth weight survivors. J Affect Disord 2016; 190: 294–9. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Mendonça M, Bartmann P, Wolke D. Very preterm birth and trajectories of domain‐specific self‐concept from childhood into adulthood. Dev Psychopathol 2022; 34: 1926–1937. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- The Eye Foundation
- Evald and Hilda Nissi Foundation
- The Finnish Medical Foundation
- Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation
- University of Oulu Graduate School
- 315690/Academy of Finland
- University of Oulu
- Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
- NNF20OC0063930/Novo Nordisk Foundation
- 46055600-159/Joint Research Committee of St. Olavs Hospital HF and the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
- 30283/Joint Research Committee of St. Olavs Hospital HF and the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
- Mary and Georg C. Ehrnrooth Foundation
- 2021/FO347467/Dam Foundation
- Sigrid Juselius Foundation
- The Alma and KA Snellman Foundation
- 90654402/Central Norway Regional Health Authority
- Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation
- 733280/European Union's Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program: Research on European Children and Adults born Preterm (RECAP Preterm)
- The Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research
- The Eye and Tissue Bank Foundation
- Foundation for Pediatric Research
- Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine, Norwegian University of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

