Application of artificial intelligence (AI) to control COVID-19 pandemic: Current status and future prospects
- PMID: 38370192
- PMCID: PMC10869876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25754
Application of artificial intelligence (AI) to control COVID-19 pandemic: Current status and future prospects
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to "Application of artificial intelligence (AI) to control COVID-19 pandemic: Current status and future prospects" [Heliyon 10 (2024) e25754].Heliyon. 2025 Feb 26;11(4):e42839. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42839. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40201302 Free PMC article.
Abstract
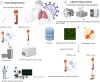
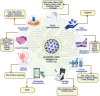
The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the everyday livelihood of people has been monumental and unparalleled. Although the pandemic has vastly affected the global healthcare system, it has also been a platform to promote and develop pioneering applications based on autonomic artificial intelligence (AI) technology with therapeutic significance in combating the pandemic. Artificial intelligence has successfully demonstrated that it can reduce the probability of human-to-human infectivity of the virus through evaluation, analysis, and triangulation of existing data on the infectivity and spread of the virus. This review talks about the applications and significance of modern robotic and automated systems that may assist in spreading a pandemic. In addition, this study discusses intelligent wearable devices and how they could be helpful throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Autonomous system; COVID-19; Healthcare system; Robotics.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- https://covid19.who.int/. Last Accessed on 19-September-2023.
-
- Arora N., Banerjee A.K., Narasu M.L. The role of artificial intelligence in tackling COVID-19. Future Medicine. 2020;15(11) doi: 10.2217/fvl-2020-0130. - DOI
-
- Petrosillo N., Viceconte G., Ergonul O., Ippolito G., Petersen E. COVID-19, SARS and MERS: are they closely related? Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2020;26(6):729–734. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.03.026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

