Synthesis rifaximin with copper (Rif-Cu) and copper oxide (Rif-CuO) nanoparticles Considerable dye decolorization: An application of aerobic oxidation of eco-friendly sustainable approach
- PMID: 38370249
- PMCID: PMC10867351
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25285
Synthesis rifaximin with copper (Rif-Cu) and copper oxide (Rif-CuO) nanoparticles Considerable dye decolorization: An application of aerobic oxidation of eco-friendly sustainable approach
Abstract
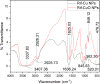
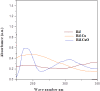
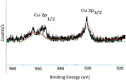
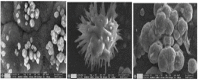
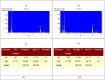
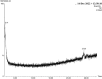
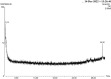
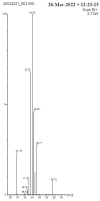
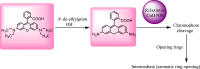
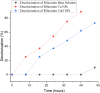
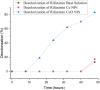
In this study, rifaximin with copper (Cu) and copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesised. The resultant CuO nanoparticles were used to degrade Rhodamine B (RhB) and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (G250). Rifaximin copper and copper oxide nanoparticles were characterised using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), and gas chromatography-electrochemical mass spectrometry (GC-EI-MS). An FT-IR study confirmed the formation of Cu in the 562 cm-1 peak range. Rifaximin Cu and CuO Nanoparticles displayed UV absorption peaks at 253 nm and 230 nm, respectively. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 was completely decolourised in Cu nanoparticles at 100 %, and Rhodamine B was also decolourised in Rifaximin CuO nanoparticles at 73 %, although Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 Rifaximin Cu nanoparticles absorbed a high percentage of dye decolorization. The aerobic oxidation of isopropanol conversion was confirmed by GC-MS analysis. Retention time of 27.35 and 30.32 was confirmed using Cu and CuO nanoparticles as the final products of 2-propanone. It is used in the textile and pharmaceutical industries for aerobic alcohol oxidation. Rifaximin CuO nanoparticles highly active in aerobic oxidation. The novelty of this study is that, for the first time, rifaximin was used for the synthesis of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles, and it successfully achieved decolorization and aerobic oxidation.
Keywords: Aerobic oxidation; Coomassie brilliant blue G250; Dye decolorization; Rhodamine B; Rifaximin Cu and CuO nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Algae-mediated copper nanocatalyst for aerobic oxidation and dye decolourization via sustainable wastewater treatment.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 13;14(1):30458. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81354-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39672817 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of omega-3 mediated copper (ω-3-Cu) and copper oxide (ω-3-CuO) nanocatalyst dual application of dye decolourization and aerobic oxidation of eco-friendly sustainable approach.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Oct;31(47):58176-58195. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34941-z. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39312113
-
Study on antibacterial alginate-stabilized copper nanoparticles by FT-IR and 2D-IR correlation spectroscopy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3597-612. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S32648. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22848180 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization of novel ZnO/CuO nanoparticles, and the applications in photocatalytic performance for rhodamine B dye degradation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Mar;29(15):22576-22588. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17106-0. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34792775
-
Current status of plant metabolite-based fabrication of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles and their applications: a review.Biomater Res. 2020 Jun 3;24:11. doi: 10.1186/s40824-020-00188-1. eCollection 2020. Biomater Res. 2020. PMID: 32514371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Algae-mediated copper nanocatalyst for aerobic oxidation and dye decolourization via sustainable wastewater treatment.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 13;14(1):30458. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81354-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39672817 Free PMC article.
-
Metal Nanoparticles Obtained by Green Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Synthesis: Characterization, Biopolymer Incorporation, and Antifungal Evaluation Against Pseudocercospora fijiensis.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 28;15(5):379. doi: 10.3390/nano15050379. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40072182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Kholany A.S., Hafith H.A., Gaber N.M. Spectrophotometric and biological studies for the interaction of rifaximin with Co, Cu, Fe and vitamin, C. J. Phys. 2022;2305(1) doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2305/1/012039. - DOI
-
- Livingston A., Trout B.L., Horvath I.T., Johnson M.D., Vaccaro L., Coronas J., Babbitt C.W., Zhang X., Pradeep T., Drioli E., J.D. Hayler Challenges and directions for green chemical engineering—role of nanoscale materials. Sustainable nanoscale engineering. 2020:1–18. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-814681-1.00001-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

