Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 as a Carcinogenic but Not a Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38370384
- PMCID: PMC10869966
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.91064
Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 as a Carcinogenic but Not a Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
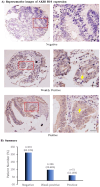
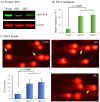
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the leading cause of cancer death, but little is known about its etiopathology. Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 (AKR1B10) protein is primarily expressed in intestinal epithelial cells, but lost in colorectal cancer tissues. This study revealed that AKR1B10 may not be a prognostic but an etiological factor in colorectal tumorigenesis. Using a tissue microarray, we investigated the expression of AKR1B10 in tumor tissues of 592 colorectal cancer patients with a mean follow-up of 25 years. Results exhibited that AKR1B10 protein was undetectable in 374 (63.13%), weakly positive in 146 (24.66%), and positive 72 (12.16%) of 592 tumor tissues. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that AKR1B10 expression was not correlated with overall survival or disease-free survival. Similar results were obtained in various survival analyses stratified by clinicopathological parameters. AKR1B10 was not correlated with tumor T-pathology, N-pathology, TNM stages, cell differentiation and lymph node/regional/distant metastasis either. However, AKR1B10 silencing in culture cells enhanced carbonyl induced protein and DNA damage; and in ulcerative colitis tissues, AKR1B10 deficiency was associated acrolein-protein lesions. Together this study suggests that AKR1B10 downregulation may not be a prognostic but a carcinogenic factor of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: AKR1B10; Biomarker; Colorectal cancer; Tissue microarrays; and DNA damage.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 protects human colon cells from DNA damage induced by electrophilic carbonyl compounds.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jan;56(1):118-129. doi: 10.1002/mc.22477. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 26969882
-
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 B10 gene silencing results in growth inhibition of colorectal cancer cells: Implication for cancer intervention.Int J Cancer. 2007 Nov 15;121(10):2301-6. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22933. Int J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17597105
-
High expression of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 is an independent predictor of favorable prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Gut Liver. 2014 Nov;8(6):648-54. doi: 10.5009/gnl13406. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Gut Liver. 2014. PMID: 25287169 Free PMC article.
-
In Search for Inhibitors of Human Aldo-Keto Reductase 1B10 (AKR1B10) as Novel Agents to Fight Cancer and Chemoresistance: Current State-of-the-Art and Prospects.J Med Chem. 2025 Jan 23;68(2):860-885. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01116. Epub 2025 Jan 5. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39757466 Review.
-
Perspective on the Structural Basis for Human Aldo-Keto Reductase 1B10 Inhibition.Metabolites. 2021 Dec 13;11(12):865. doi: 10.3390/metabo11120865. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34940623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily website and database: An update.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Aug 1;398:111111. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111111. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38878851 Free PMC article.
-
AKR1B10 and digestive tumors development: a review.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 16;15:1462174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462174. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39737179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E. et al. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:8–29. - PubMed
-
- Rennert G. Prevention and early detection of colorectal cancer-new horizons. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007;174:179–87. - PubMed
-
- Hawk ET, Levin B. Colorectal cancer prevention. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:378–91. - PubMed
-
- Collins RH Jr, Feldman M, Fordtran JS. Colon cancer, dysplasia, and surveillance in patients with ulcerative colitis. A critical review. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1654–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

