Moringa oleifera (drumstick tree)-nutraceutical, cosmetological and medicinal importance: a review
- PMID: 38370483
- PMCID: PMC10869624
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1288382
Moringa oleifera (drumstick tree)-nutraceutical, cosmetological and medicinal importance: a review
Abstract
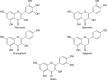
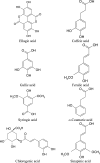
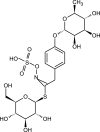
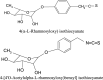
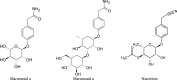
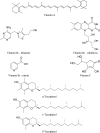
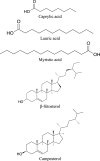
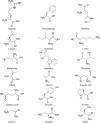
Moringa oleifera Lam. (Moringaceae) is a species of tree with an increasing utility, occurring naturally mainly in Pakistan and northern India. M. oleifera is currently cultivated in Africa, South America, Asia and the Middle East. The usage of its leaves, seed oil, bark, fruits, flowers and roots has positive opinions of FDA (American Food and Drug Administration), EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and CosIng (Cosmetic Ingredients database). The chemical composition of M. oleifera is dominated by: proteins (consisting mainly of amino acids such as arginine or serine), fatty acids (omega-3 and omega-6), vitamins (vitamin A, B and C and tocopherols), mineral salts (including several bioelements, such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium), valuable polyphenolic compounds from the group of phenolic acids (e.g., gallic acid, ferulic acid) and flavonoids (e.g., myricetin, rutoside, and kaempferol). The raw materials show antioxidant, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. Dietary supplements and alimentary products containing M. oleifera are recommended as health-promoting and "novel food" preparations. The main purpose of this work was a review of the latest scientific literature on M. oleifera, with particular emphasis on the studies focusing on its chemical composition, biological activity and safety. Moreover, the review tends to discuss the results of biotechnological studies using this material and the agronomical significance.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; agronomic importance; chemical composition; cosmetology applications; drumstick tree; nutritional properties; pharmacological activities.
Copyright © 2024 Klimek-Szczykutowicz, Gaweł-Bęben, Rutka, Blicharska, Tatarczak-Michalewska, Kulik-Siarek, Kukula-Koch, Malinowska and Szopa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nature's Gold (Moringa Oleifera): Miracle Properties.Cureus. 2022 Jul 7;14(7):e26640. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26640. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35949760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moringa oleifera: a food plant with multiple medicinal uses.Phytother Res. 2007 Jan;21(1):17-25. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2023. Phytother Res. 2007. PMID: 17089328 Review.
-
Biological, nutritional, and therapeutic significance of Moringa oleifera Lam.Phytother Res. 2019 Nov;33(11):2870-2903. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6475. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Phytother Res. 2019. PMID: 31453658 Review.
-
Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Lam.J Pharmacopuncture. 2017 Sep;20(3):194-200. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2017.20.022. Epub 2017 Sep 30. J Pharmacopuncture. 2017. PMID: 30087795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive components from Moringa oleifera seeds: production, functionalities and applications - a critical review.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022 Mar;42(2):271-293. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1931804. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34151645 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Effect of Moringa oleifera Seed Extract and Its Behenic Acid Component on Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;14(1):19. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010019. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39858305 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects and mechanism of myricetin in liver diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Apr;31(4):87. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13452. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39917997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Nutritional Powerhouse with Multifaceted Pharmacological and Functional Applications.Life (Basel). 2025 May 29;15(6):881. doi: 10.3390/life15060881. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract, probing antibacterial and antioxidant activities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08839-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595209 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Miracle Tree: Therapeutic Potential of Moringa oleifera in Chronic Disease Management and Beyond.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 5;13(3):634. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030634. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abioye V. F., Mo A. (2015). Proximate composition and sensory properties of Moringa fortified maize-ogi. J. Nutr. Food Sci. s12, 1–4. 10.4172/2155-9600.s12-001 - DOI
-
- Adedapo A. A., Mogbojuri O. M., Emikpe B. O. (2009). Safety evaluations of the aqueous extract of the leaves of Moringa oleifera in rats. J. Med. Plant Res. 3, 586–591.
-
- Afuang W., Siddhuraju P., Becker K. (2003). Comparative nutritional evaluation of raw, methanol extracted residues and methanol extracts of moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves on growth performance and feed utilization in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquac. Res. 34, 1147–1159. 10.1046/j.1365-2109.2003.00920.x - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

