This is a preprint.
Single-cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Identified Fatty Acid-binding Proteins Controlling Endothelial Glycolytic and Arterial Programming in Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 38370670
- PMCID: PMC10871348
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.02.11.579846
Single-cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Identified Fatty Acid-binding Proteins Controlling Endothelial Glycolytic and Arterial Programming in Pulmonary Hypertension
Update in
-
Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Identified Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins Controlling Endothelial Glycolytic and Arterial Programming in Pulmonary Hypertension.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 Jul;45(7):1145-1165. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321173. Epub 2025 May 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 40401371 Free PMC article.
Abstract
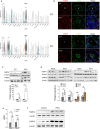
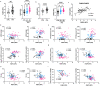
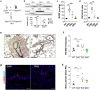
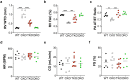
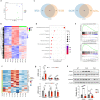
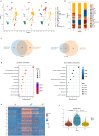
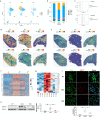
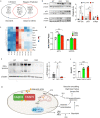
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a devastating disease characterized by obliterative vascular remodeling and persistent increase of vascular resistance, leading to right heart failure and premature death. Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms will help develop novel therapeutic approaches for PAH patients. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) analysis found that both FABP4 and FABP5 were highly induced in endothelial cells (ECs) of Egln1 Tie2Cre (CKO) mice, which was also observed in pulmonary arterial ECs (PAECs) from idiopathic PAH (IPAH) patients, and in whole lungs of pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats. Plasma levels of FABP4/5 were upregulated in IPAH patients and directly correlated with severity of hemodynamics and biochemical parameters using plasma proteome analysis. Genetic deletion of both Fabp4 and 5 in CKO mice (Egln1 Tie2Cre /Fabp4-5 -/- ,TKO) caused a reduction of right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and RV hypertrophy, attenuated pulmonary vascular remodeling and prevented the right heart failure assessed by echocardiography, hemodynamic and histological analysis. Employing bulk RNA-seq and scRNA-seq, and spatial transcriptomic analysis, we showed that Fabp4/5 deletion also inhibited EC glycolysis and distal arterial programming, reduced ROS and HIF-2α expression in PH lungs. Thus, PH causes aberrant expression of FABP4/5 in pulmonary ECs which leads to enhanced ECs glycolysis and distal arterial programming, contributing to the accumulation of arterial ECs and vascular remodeling and exacerbating the disease.
Keywords: arterial; glycolysis; hypoxia; lipid metabolism; right heart failure.
Figures

References
-
- Humbert M, Guignabert C, Bonnet S, Dorfmüller P, Klinger JR, Nicolls MR, Olschewski AJ, Pullamsetti SS, Schermuly RT, Stenmark KR, Rabinovitch M. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: state of the art and research perspectives. The European respiratory journal. 2019;53:1801887. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paulin R, Michelakis ED. The metabolic theory of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation Research. 2014;115:148–164. - PubMed
-
- Nickel NP, Yuan K, Dorfmuller P, Provencher S, Lai YC, Bonnet S, Austin ED, Koch CD, Morris A, Perros F, Montani D, Zamanian RT, De Jesus Perez VA. Beyond the lungs: Systemic manifestations of pulmonary arterial hypertension. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2020;201:148–157. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
