Recurrent Plunging Ranula Due to a Sublingual Ectopic Gland: A Rare Clinical Entity
- PMID: 38371149
- PMCID: PMC10874684
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.52590
Recurrent Plunging Ranula Due to a Sublingual Ectopic Gland: A Rare Clinical Entity
Abstract
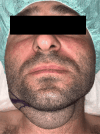
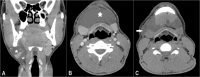
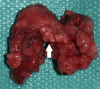
Ranula is a benign cystic lesion caused by the escape and collection of salivary mucus. Classically, it is divided into simple ranulas, a cystic mass in the floor of the mouth, and diving/plunging/cervical ranulas, a submandibular mass without apparent intraoral involvement. Although plunging ranula is a well-documented cause of neck swelling, its association with the presence of ectopic sublingual glands is extremely rare, with less than five cases reported. Other cervical cystic lesions may have the same clinical aspect; therefore, advanced diagnostic techniques like a CT scan or MRI play a critical role in early diagnosis. Different approaches have been used to treat ranulas, including non-invasive, minimally invasive, and surgical techniques. The purpose of this paper is to highlight a case report of a giant plunging ranula due to an anatomical aberration of the right sublingual gland, along with a significant literature review.
Keywords: ectopic gland; mouth floor; plunging ranula; salivary gland; tail sign; transoral surgical approach.
Copyright © 2024, Rodrigues Barros et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Plunging ranula. Review (Article in French) Pouzoulet P, Collet C, Foletti JM, Guyot L, Chossegros C. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2016;117:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Horseshoe shaped, anterior crossing ranula, a case report. El Beltagi AH, Al Far ESA, Al Sahmmary N. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2007;64:95–98.
-
- Clinical review of 580 ranulas. Zhao YF, Jia Y, Chen XM, Zhang WF. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15356464/ Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004;98:281–287. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
