ZJU Index as a Predictive Tool for Diabetes Incidence: Insights from a Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 38371391
- PMCID: PMC10873143
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S446042
ZJU Index as a Predictive Tool for Diabetes Incidence: Insights from a Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: In previous studies, the ZJU index was reported to be a superior predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese population compared to the Fatty Liver Index. However, whether the ZJU Index is significantly associated with diabetes among Asian populations has not been determined.
Methods: The NAGALA study was carried out at Murakami Memorial Hospital (Gifu, Japan) beginning in 1994. This study included the data of the subjects who underwent health check-ups from 2004 to 2015. The ZJU Index comprises body mass index (BMI), fasting plasma glucose, triglyceride, and alanine aminotransferase-to-aspartate aminotransferase (ALT) levels and an adjustment point for females. We conducted Cox proportional hazard regression to evaluate the association between quartiles of the ZJU Index and the risk of incident diabetes.
Participants: A total of 15,464 individuals who underwent health check-ups were included in this study.
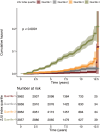
Results: A total of 373 cases of incident diabetes were documented during 93,350 person-years of follow-up. As the ZJU index increased, the incidence of diabetes gradually increased (P <0.001). According to the multivariable model adjusted for metabolic covariates, the fourth quartile of the ZJU Index was positively associated with the risk of diabetes compared to the first quartile (HR=2.519, 95% CI=1.297-4.891). Subgroup analysis revealed that the association between the ZJU index and diabetes risk was significant in subjects aged younger than 40 years (HR=3.327, 95% CI=1.544-7.171), in females (HR=4.480, 95% CI=1.302-15.419), in individuals with a BMI<25 kg/m2 (HR=3.812, 95% CI=1.992-7.293) and in individuals with a nonregular exercise (HR=2.479, 95% CI=1.193-5.152).
Conclusion: We observed a positive association between the ZJU Index and incident diabetes in the general population.
Keywords: ZJU index; diabetes; epidemiology.
© 2024 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between the ZJU index and risk of new-onset non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obese participants: a Chinese longitudinal prospective cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 9;15:1340644. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1340644. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38405152 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-response association of the ZJU index and fatty liver disease risk: A large cohort in China.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;36(5):1326-1333. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15286. Epub 2020 Oct 14. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33001484
-
Risk for the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Aug;33(8):1518-1523. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14105. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29381226
-
The ZJU index: a useful indicator for recognizing insulin resistance in the Chinese general population.Acta Diabetol. 2016 Oct;53(5):817-23. doi: 10.1007/s00592-016-0878-5. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Acta Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 27393006
-
AST to ALT ratio and arterial stiffness in non-fatty liver Japanese population:a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Dec 3;17(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0920-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30509277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Insights into the Association of ZJU index with Periodontitis in US participants: a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jul 17;24(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02655-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40676601 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the efficacy of the ZJU index and triglyceride‒glucose product index in identifying obstructive sleep apnea hypoventilation syndrome in patients with metabolic syndrome.Hormones (Athens). 2025 Jun;24(2):477-485. doi: 10.1007/s42000-025-00643-5. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Hormones (Athens). 2025. PMID: 40116990
-
ZJU index as a predictive biomarker of gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 13;12:1570771. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1570771. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40584102 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear association of a composite metabolic index (ZJU index) with hypertension: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2003-2018.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 18;12:1608648. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1608648. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40606025 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials