Diarrhea induced by insufficient fat absorption in weaned piglets: Causes and nutrition regulation
- PMID: 38371473
- PMCID: PMC10869582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.12.004
Diarrhea induced by insufficient fat absorption in weaned piglets: Causes and nutrition regulation
Abstract
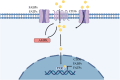
Fat is one of the three macronutrients and a significant energy source for piglets. It plays a positive role in maintaining intestinal health and improving production performance. During the weaning period, physiological, stress and diet-related factors influence the absorption of fat in piglets, leading to damage to the intestinal barrier, diarrhea and even death. Signaling pathways, such as fatty acid translocase (CD36), pregnane X receptor (PXR), and AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK), are responsible for regulating intestinal fat uptake and maintaining intestinal barrier function. Therefore, this review mainly elaborates on the reasons for diarrhea induced by insufficient fat absorption and related signaling pathways in weaned-piglets, with an emphasis on the intestinal fat absorption disorder. Moreover, we focus on introducing nutritional strategies that can promote intestinal fat absorption in piglets with insufficient fat absorption-related diarrhea, such as lipase, amino acids, and probiotics.
Keywords: Diarrhea; Fat absorption; Nutrient regulation; Weaned piglet.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, and there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the content of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Asadi Shahmirzadi A., Edgar D., Liao C.Y., Hsu Y.M., Lucanic M., Asadi Shahmirzadi A., Wiley C.D., Gan G., Kim D.E., Kasler H.G., Kuehnemann C., Kaplowitz B., Bhaumik D., Riley R.R., Kennedy B.K., Lithgow G.J. Alpha-ketoglutarate, an endogenous metabolite, extends lifespan and compresses morbidity in aging mice. Cell Metab. 2020;32:447–456 e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bach Korsholm Knudsen K., Heerup C., Rongaard Stange Jensen T., Geng X., Drachmann N., Nordby P., Bekker Jeppesen P., Ifaoui I., Mullertz A., Torp Sangild P., Stampe Ostenfeld M., Thymann T. Bovine milk-derived emulsifiers increase triglyceride absorption in newborn formula-fed pigs. Nutrients. 2021;13(2):410. doi: 10.3390/nu13020410. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balamurugan K., Medishetti R., Kotha J., Behera P., Chandra K., Mavuduru V.A., Joshi M.B., Samineni R., Katika M.R., Ball W.B., Thondamal M., Challa A., Chatti K., Parsa K.V.L. PHLPP1 promotes neutral lipid accumulation through AMPK/ChREBP-dependent lipid uptake and fatty acid synthesis pathways. iScience. 2022;25(2) doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

