Clinical factors for delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae from acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a retrospective study
- PMID: 38371510
- PMCID: PMC10869438
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1333197
Clinical factors for delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae from acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae (DNS), which seriously affect the daily lives of patients, are the most common complications of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. No uniform screening tool is available for identifying high-risk groups. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to explore whether conventional laboratory indicators and imaging data from primary hospitals could predict the occurrence of DNS.
Methods: This retrospective observational study was conducted in a single-center primary hospital from January 1, 2021 to May 31, 2023. Participants included patients aged >18 years with acute CO poisoning. Patients with complete recovery in the acute phase were followed up by telephone and outpatient visits, and the presence of DNS was determined according to the occurrence of new neurological symptoms within 6 weeks after discharge. We obtained demographic, laboratory, and imaging data from the medical records and performed a univariate analysis. A multivariate logistic regression model was used to identify independent clinical predictors of DNS.
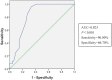
Results: A total of 73 patients were included in the study, of whom 25 (34.2%) developed DNS. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that a longer duration of CO exposure (adjusted odds ratio (AOR): 1.262, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.069-1.490) and the presence of acute brain lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) (AOR: 5.117, 95% CI: 1.430-18.315) were independent risk factors for DNS. Receiver operating characteristic analyses of the duration of CO exposure were performed (area under the curve (AUC): 0.825; 95% CI: 0.731-0.918) with a cut-off value of 5.5 h, and DNS was predicted with a sensitivity of 96% and a specificity of 66.7%.
Conclusion: High cranial DWI signal within 24 h and duration of poisoning longer than 5.5 h are independent predictors of DNS. The predictive effects of conventional laboratory indicators require further standardized and large-sample studies.
Keywords: carbon monoxide poisoning; delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae; diffusion-weighted imaging; exposure duration; laboratory indicators.
Copyright © 2024 Gao, Wei and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting optimal time for hyperbaric oxygen therapy following carbon monoxide poisoning for prevention of delayed neuropsychiatric sequelae: A retrospective study.J Neurol Sci. 2019 Jan 15;396:187-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2018.11.025. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30481656
-
Clinical predictors of delayed neurological sequelae in charcoal-burning carbon monoxide poisoning.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Oct;48:12-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33838469
-
Predictive Role of QTc Prolongation in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning-Related Delayed Neuropsychiatric Sequelae.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 25;2018:2543018. doi: 10.1155/2018/2543018. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30356348 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of Glasgow Coma Scale with Delayed Neuropsychiatric Sequelae in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Systematic Review.J Emerg Med. 2025 Jun;73:112-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2025.01.006. Epub 2025 Jan 18. J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40348692
-
Association between Early Phase Serum Lactate Levels and Occurrence of Delayed Neuropsychiatric Sequelae in Adult Patients with Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 18;12(4):651. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040651. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455767 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed Postanoxic Encephalopathy Following Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 May 13;17(5):e84024. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84024. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40519477 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning: a literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 26;12:1559264. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1559264. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40206479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources