ERK/MEK Pathway Regulates Th17 Cell Differentiation in Patients with Pemphigus Vulgaris
- PMID: 38371571
- PMCID: PMC10868988
- DOI: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_924_22
ERK/MEK Pathway Regulates Th17 Cell Differentiation in Patients with Pemphigus Vulgaris
Abstract
Background: T helper (Th) cells are involved in the pathogenesis of pemphigus vulgaris (PV). However, the mechanism still needs more exploration.
Aims: This study aimed to evaluate the molecular mechanism of the dysregulation of Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of patients with PV.
Materials and methods: Serum levels of IL-17 and anti-Dsg3 titres in patients with PV were analysed using ELISA. The mRNA expression of retinoic acid orphan receptor γt (RORγt) in CD4+ T cells was detected using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (qPCR). The number of Th17 cells was examined using flow cytometry. Western blot analysis and immunofluorescent staining were also performed to investigate the expression levels of ERK/MAPK signalling proteins and Th17 lineage-associated proteins.
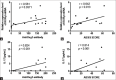
Results: The proportion of Th17 cells and Th17 spectrum-associated proteins (p-STAT3, RORγt and IL-17) were upregulated in CD4+ cells in PV patients. The increased transcriptional levels of RORγt and IL-17 correlated positively with the severity of PV. Elevated phosphorylation of the ERK signalling factors was found in the collected CD4+ T cells in PV patients. The inhibition of the ERK signalling pathway significantly reduced the differentiation of Th17 cells in PV patients in vitro.
Conclusion: Th17 cells are essential in the dysregulation of PV, and ERK signalling is involved in Th17-type immunity and promotes the development of PV. The study here provides us with a potential therapeutic target for PV.
Keywords: ERK signalling; Th17 cell; pemphigus vulgaris.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Journal of Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Melchionda V, Harman KE. Pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus: An overview of the clinical presentation, investigations and management. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:740–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
