Carborane-Containing Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications
- PMID: 38371730
- PMCID: PMC10870755
- DOI: 10.1021/acspolymersau.3c00030
Carborane-Containing Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
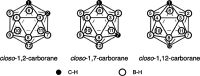
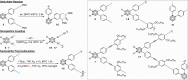
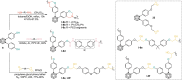
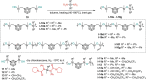
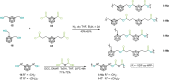
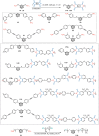
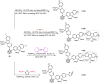
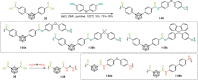
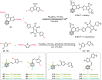
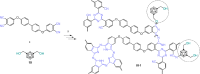
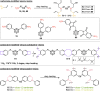
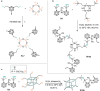
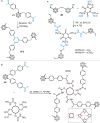
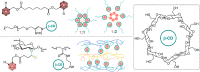
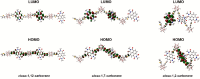
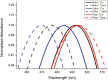
Carboranes are an important class of electron-delocalized icosahedral carbon-boron clusters with unique physical and chemical properties, which can offer various functions to polymers including enhanced heat-resistance, tuned electronic properties and hydrophobicity, special ability of dihydrogen bond formation, and thermal neutron capture. Carborane-containing polymers have been synthesized mainly by means of step-growth polymerizations of disubstituted carborane monomers, with chain-growth polymerizations of monosubstituted carborane monomers including ATRP, RAFT, and ROMP only utilized recently. Carborane-containing polymers may find application as harsh-environment resistant materials, ceramic precursors, fluorescent materials with tuned emissive properties, novel optoelectronic devices, potential BNCT agents, and drug carriers with low cytotoxicity. This review highlights carborane-containing polymer synthesis strategies and potential applications, showcasing the versatile properties and possibilities that this unique family of boron compounds can provide to the polymeric systems.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






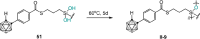




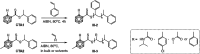
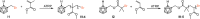
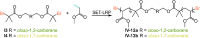
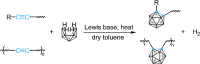


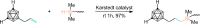
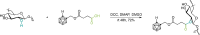

References
-
- Young R. J.; Lovell P. A.. Introduction to Polymers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 201110.1201/9781439894156. - DOI
-
- Grimes R. N.Introduction and History. In Carboranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2016; pp 1–510.1016/B978-0-12-801894-1.00001-9. - DOI
-
- Grimes R. N. Small Carboranes. Carboranes 2016, 23–87. 10.1016/B978-0-12-801894-1.00004-4. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
