Three-dimension model of root canal morphology of primary maxillary incisors by micro-computed tomography study
- PMID: 38371975
- PMCID: PMC10873741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25890
Three-dimension model of root canal morphology of primary maxillary incisors by micro-computed tomography study
Abstract
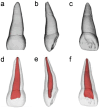
The success of root canal treatment for deciduous teeth depends upon the shape of the root canal, among other factors. Despite this, there are limited reports on the use of high-resolution micro-CT to describe the root canal morphology of primary maxillary incisors. In this study, we aimed to create a three-dimensional (3D) digital model of the root canal morphology of primary maxillary incisors using microcomputed tomography (micro-CT). To provide a reference for the development of restorative posts for the primary maxillary incisors. Primary maxillary central and lateral incisors (n = 10 each) were analysed. Micro-computed tomography was used to conduct 3D analyses of the root canal system of the primary maxillary incisors. The canal volume and surface area of the primary maxillary central incisors were larger than those of the primary maxillary lateral incisors. The structural model index value was significantly lower in central incisors. At the cervical level and the interface between the cervical and middle one-third cross-sectional levels, the root canals of the primary maxillary lateral incisors were significantly rounder. The labio-palatal dimension and the diameters of the central incisors at the four different levels were significantly smaller than the diameter of the mesio-distal dimension. The taper of the central and lateral incisors gradually increased from the apical one-third to the cervical one-third in the labio-palatal dimension. The data obtained from the 3D analysis of maxillary incisors in this study will contribute to the design of root canal posts.
Keywords: Micro-computed tomography; Morphology; Primary maxillary incisors; Root canal system.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Tinanoff N., et al. Early childhood caries epidemiology, aetiology, risk assessment, societal burden, management, education, and policy: global perspective. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2019;29(3):238–248. - PubMed
-
- Haber J., Hartnett E. The interprofessional role in dental caries management: impact of the nursing profession in early childhood caries. Dent Clin North Am. 2019;63(4):653–661. - PubMed
-
- Sakaryali D., et al. Evaluation of the impact of early childhood caries, traumatic dental injury, and malocclusion on oral health-Related quality of life for Turkish preschool children and families. Niger J Clin Pract. 2019;22(6):817–823. - PubMed
-
- Judd P.L., et al. Composite resin short-post technique for primary anterior teeth. J Am Dent Assoc. 1990;120(5):553–555. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

