Functional parcellation of the neonatal cortical surface
- PMID: 38372292
- PMCID: PMC10875653
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhae047
Functional parcellation of the neonatal cortical surface
Abstract
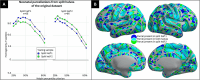
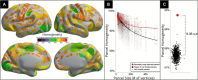
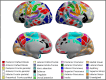
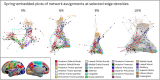
The cerebral cortex is organized into distinct but interconnected cortical areas, which can be defined by abrupt differences in patterns of resting state functional connectivity (FC) across the cortical surface. Such parcellations of the cortex have been derived in adults and older infants, but there is no widely used surface parcellation available for the neonatal brain. Here, we first demonstrate that existing parcellations, including surface-based parcels derived from older samples as well as volume-based neonatal parcels, are a poor fit for neonatal surface data. We next derive a set of 283 cortical surface parcels from a sample of n = 261 neonates. These parcels have highly homogenous FC patterns and are validated using three external neonatal datasets. The Infomap algorithm is used to assign functional network identities to each parcel, and derived networks are consistent with prior work in neonates. The proposed parcellation may represent neonatal cortical areas and provides a powerful tool for neonatal neuroimaging studies.
Keywords: cortical areas; fMRI; functional connectivity; neonate; parcellation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permission@oup.com.
Figures


Update of
-
Functional parcellation of the neonatal brain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 11:2023.11.10.566629. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.10.566629. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jan 31;34(2):bhae047. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae047. PMID: 37986902 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Alexander B, Murray AL, Loh WY, Matthews LG, Adamson C, Beare R, Chen J, Kelly CE, Rees S, Warfield SK, et al. . A new neonatal cortical and subcortical brain atlas: the Melbourne Children’s regional infant brain (M-CRIB) atlas. NeuroImage. 2017:147:841–851. - PubMed
-
- Arslan S, Ktena SI, Makropoulos A, Robinson EC, Rueckert D, Parisot S. Human brain mapping: a systematic comparison of parcellation methods for the human cerebral cortex. NeuroImage. 2018:170:5–30. - PubMed
-
- Beucher S, Lantuejoul C. Use of watersheds in contour detection. Presented at the international workshop on image processing: real-time edge and motion detection/estimation. Rennes, France, 1979.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

