Myths and Methodologies: Understanding the health impact of head down bedrest for the benefit of older adults and astronauts. Study protocol of the Canadian Bedrest Study
- PMID: 38372420
- PMCID: PMC11061626
- DOI: 10.1113/EP091473
Myths and Methodologies: Understanding the health impact of head down bedrest for the benefit of older adults and astronauts. Study protocol of the Canadian Bedrest Study
Abstract
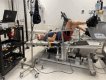
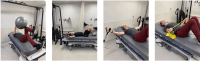
Weightlessness during spaceflight can harm various bodily systems, including bone density, muscle mass, strength and cognitive functions. Exercise appears to somewhat counteract these effects. A terrestrial model for this is head-down bedrest (HDBR), simulating gravity loss. This mirrors challenges faced by older adults in extended bedrest and space environments. The first Canadian study, backed by the Canadian Space Agency, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Canadian Frailty Network, aims to explore these issues. The study seeks to: (1) scrutinize the impact of 14-day HDBR on physiological, psychological and neurocognitive systems, and (2) assess the benefits of exercise during HDBR. Eight teams developed distinct protocols, harmonized in three videoconferences, at the McGill University Health Center. Over 26 days, 23 participants aged 55-65 underwent baseline measurements, 14 days of -6° HDBR, and 7 days of recovery. Half did prescribed exercise thrice daily combining resistance and endurance exercise for a total duration of 1 h. Assessments included demographics, cardiorespiratory fitness, bone health, body composition, quality of life, mental health, cognition, muscle health and biomarkers. This study has yielded some published outcomes, with more forthcoming. Findings will enrich our comprehension of HDBR effects, guiding future strategies for astronaut well-being and aiding bedrest-bound older adults. By outlining evidence-based interventions, this research supports both space travellers and those enduring prolonged bedrest.
Keywords: bedrest; exercise countermeasure; older adults; space health.
© 2024 The Authors. Experimental Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aragón, L. F. (2000). Evaluation of four vertical jump tests: Methodology, reliability, validity, and accuracy. Measurement in Physical Education and Exercise Science, 4(4), 215–228.
-
- Badhwar, A. , Collin‐Verreault, Y. , Orban, P. , Urchs, S. , Chouinard, I. , Vogel, J. , Potvin, O. , Duchesne, S. , & Bellec, P. (2020). Multivariate consistency of resting‐state fMRI connectivity maps acquired on a single individual over 2.5 years, 13 sites and 3 vendors. NeuroImage, 205, 116210. - PubMed
-
- Balbim, G. M. , Falck, R. S. , Barha, C. K. , Tai, D. , Best, J. R. , Hajj‐Boutros, G. , Madden, K. , & Liu‐Ambrose, T. (2024). Exercise counters the negative impact of bed rest on executive functions in middle‐aged and older adults: A proof‐of‐concept randomized controlled trial. Maturitas, 179, 107869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources