Anogenital distance in a cohort of 169 infant boys with uni- or bilateral cryptorchidism including 18 boys with vanishing testes
- PMID: 38373213
- PMCID: PMC10988100
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/deae025
Anogenital distance in a cohort of 169 infant boys with uni- or bilateral cryptorchidism including 18 boys with vanishing testes
Abstract
Study question: Do different boys with different types of cryptorchidism exhibit different anogenital distances (AGDs)?
Summary answer: Length of AGD seemed to differ in different groups of patients with cryptorchidism.
What is known already: AGD, which is used as an indicator of prenatal androgen action, tends to be shorter in boys with cryptorchidism compared to unaffected boys. Shorter AGDs have also been reported in boys with hypospadias, in men with poor semen quality, and in men with testicular cancer.
Study design, size, duration: A prospective descriptive cohort study was performed using data from consecutively selected boys with cryptorchidism (n = 169) operated in a single center over a period of 3 years (September 2019 to October 2022).
Participants/materials, setting, methods: AGD was measured in 169 infant boys, at 3 to 26 months of age, during anesthesia with a vernier caliper measuring the distance from the anus to the base of the scrotum (AGDAS) and from the anus to the anterior base of the penis (AGDAP) in two body positions according to the methods by 'The Infant Development and the Environment Study' (TIDES) and 'Cambridge Baby Growth Study', resulting in four mean values per patient (TIDES AGDAS/AP and Cambridge AGDAS/AP). Normal values for AGD by age were set by our hospital Department of Growth and Reproduction based on a large cohort of healthy infant boys (n = 1940). Testicular biopsies were performed at orchidopexy as a clinical routine. The germ cell number (G/T) and type Ad spermatogonia number (AdS/T) per cross-sectional tubule of at least 100 and 250 tubules, respectively were measured and related to normal samples. Blood samples were obtained by venipuncture for measuring serum LH, FSH, and inhibin B. They were analyzed in our hospital Department of Growth and Reproduction where the normal reference was also established. Correlations between the four mean AGD measurements for each boy were evaluated by Spearman rank correlation analyses. The AGD measurement of every boy was transferred to the multiple of the median (MoM) of the normal AGD for age and named MoM AGD.
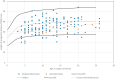
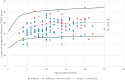
Main results and the role of chance: There were 104 boysoperated for unilateral, and 47 boys operated for bilateral, undescended testes, whereas 18 boys had vanished testis including one boy with bilateral vanished testes. Only 6% of cases with vanished testes had a MoM AGD higher than the normal median compared to 32% with undescended testes (P < 0.05). MoM AGD increased with the age at surgery for boys with vanished testis (Spearman r = 0.44), but not for boys with undescended testes (Spearman r = 0.14). Boys with bilateral cryptorchidism had longer AGDs and more often had hypogonadotropic hypogonadism than boys with unilateral cryptorchidism (P < 0.005) and (P < 0.000001).
Limitations, reasons for caution: Although being the largest published material of AGD measurements of infant boys with cryptorchidism, one limitation of this study covers the quite small number of patients in the different groups, which may decrease the statistical power. Another limitation involves the sparse normal reference material on G/T and AdS/T. Finally, there are currently no longitudinal studies evaluating AGD from birth to adulthood and evaluating childhood AGD in relation to fertility outcome. Our study is hypothesis generating and therefore the interpretation of the results should be regarded as exploratory rather than reaching definite conclusions.
Wider implications of the findings: The study findings are in agreement with literature as the total included group of boys with cryptorchidism exhibited shorter than normal AGDs. However, new insights were demonstrated. Boys with vanished testis had shorter AGDs compared to unaffected boys and to boys with undescended testes. This finding challenges the current concept of AGD being determined in 'the masculinization programming window' in Week 8 to 14 of gestation. Furthermore, boys with bilateral cryptorchidism had longer AGDs and more often had hypogonadotropic hypogonadism than boys with unilateral cryptorchidism, suggesting that the lack of fetal androgen in hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is not that significant.
Study funding/competing interest(s): No external funding was used and no competing interests are declared.
Trial registration number: The trial was not registered in an ICMJE-recognized trial registry.
Keywords: androgen; anogenital distance; cryptorchidism; germ cells; gonadotropins; testes.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Testicular cancer survivors have shorter anogenital distance that is not increased by 1 year of testosterone replacement therapy.Hum Reprod. 2021 Aug 18;36(9):2443-2451. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deab162. Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34223605 Clinical Trial.
-
Shorter anogenital distance correlates with undescended testis: a detailed genital anthropometric analysis in human newborns.Hum Reprod. 2013 Sep;28(9):2343-9. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det286. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23838161
-
Shorter anogenital distance correlates with the severity of hypospadias in pre-pubertal boys.Hum Reprod. 2016 Jul;31(7):1406-10. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew115. Epub 2016 May 10. Hum Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27165620
-
Anogenital distance as a marker of androgen exposure in humans.Andrology. 2016 Jul;4(4):616-25. doi: 10.1111/andr.12156. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Andrology. 2016. PMID: 26846869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptorchidism: a morphological study of 670 biopsies.Helv Paediatr Acta. 1987 Oct;42(2-3):145-58. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1987. PMID: 2891637 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocrine disruption and male reproductive disorders: unanswered questions.Hum Reprod. 2024 Sep 1;39(9):1879-1888. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae143. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38926156 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Backhouse KM. Development and descent of the testis. Eur J Pediatr 1982;139:249–252. - PubMed
-
- Bader MI, Peeraully R, Ba'ath M, McPartland J, Baillie C.. The testicular regression syndrome—do remnants require routine excision? J Pediatr Surg 2011;46:384–386. - PubMed
-
- Barnea ER, Shurtz-Swirski R.. Modification of pulsatile human chorionic gonadotrophin secretion in first trimester placental explants induced by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Hum Reprod 1992;7:305–310. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

