Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of Vernonia arborea accelerate the healing of infected wounds in adult Zebrafish
- PMID: 38373996
- PMCID: PMC10875872
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04383-8
Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of Vernonia arborea accelerate the healing of infected wounds in adult Zebrafish
Abstract
Background: Management of wounds and healing under impaired conditions are the major challenges faced globally by healthcare workers. Phytocompounds which are anti-microbial and capable of modulating inflammation contribute to overall wound healing and regain of the lost structure and function especially in wounds impaired with polymicrobial infection.
Methods: An acute cutaneous impaired wound model using adult zebrafish was validated to simulate mammalian wound pathophysiology. This model was used to evaluate phytofractions of Vernonia arborea in the present study, for reduction of infection; myeloperoxidase (MPO) as a marker of infection; neutrophil infiltration and resolution; kinetics of inflammatory cytokines; and wound repair kinetics (viz., nitrite levels and iNoS expression; reepithelisation).
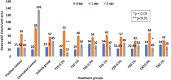
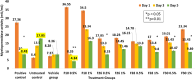
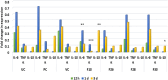
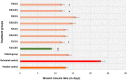
Results: Four fractions which were active in-vitro against five selected wound microbes were shown to reduce ex-vivo microbial bioburden upto 96% in the infected wound tissue. The reduction in CFU correlated with the neutrophil kinetics and MPO enzyme levels in the treated, wound infected zebrafish. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and TNF-α) was downregulated while upregulating anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10), and nitric oxide signalling with fourfold increase in iNOS expression. The adult zebrafish wound model could well serve as a standard tool for assessing phytoextracts such as V. arborea for wound healing with anti-microbial properties.
Keywords: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; Interleukins; Myeloperoxidase; Neutrophil; Wound infection; Zebrafish.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Amelioration of TPA-induced skin inflammation by the leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina involves ERK/STAT3 (Ser727) signaling inhibition.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul 20;102:154194. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154194. Epub 2022 May 23. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35660348
-
Systematic investigation of ethanolic extract from Leea macrophylla: Implications in wound healing.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;191:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.034. Epub 2016 Jun 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27321280
-
Evaluation of the wound healing properties of South African medicinal plants using zebrafish and in vitro bioassays.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 25;286:114867. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114867. Epub 2021 Nov 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34822956
-
[The modern approach to wound treatment].Med Pregl. 2000 Jul-Aug;53(7-8):363-8. Med Pregl. 2000. PMID: 11214479 Review. Croatian.
-
Zebrafish as a Model System to Study the Mechanism of Cutaneous Wound Healing and Drug Discovery: Advantages and Challenges.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 18;14(10):1058. doi: 10.3390/ph14101058. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sachdeva C, Satyamoorthy K, Murali TS. Microbial interplay in skin and chronic wounds. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2022;9:21–31. doi: 10.1007/s40588-022-00180-4. - DOI
-
- Pogson K, Nurczyk K, Slijivic S, Jones SW, Cairns B, Nizamani R, et al. 716 increased mortality in burn center admissions with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Burn Care Res. 2020;41(1):S189–S190. doi: 10.1093/jbcr/iraa024.302. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

