Pleiotropic contribution of rbfox1 to psychiatric and neurodevelopmental phenotypes in two zebrafish models
- PMID: 38374212
- PMCID: PMC10876957
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-02801-6
Pleiotropic contribution of rbfox1 to psychiatric and neurodevelopmental phenotypes in two zebrafish models
Abstract
RBFOX1 is a highly pleiotropic gene that contributes to several psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders. Both rare and common variants in RBFOX1 have been associated with several psychiatric conditions, but the mechanisms underlying the pleiotropic effects of RBFOX1 are not yet understood. Here we found that, in zebrafish, rbfox1 is expressed in spinal cord, mid- and hindbrain during developmental stages. In adults, expression is restricted to specific areas of the brain, including telencephalic and diencephalic regions with an important role in receiving and processing sensory information and in directing behaviour. To investigate the contribution of rbfox1 to behaviour, we used rbfox1sa15940, a zebrafish mutant line with TL background. We found that rbfox1sa15940 mutants present hyperactivity, thigmotaxis, decreased freezing behaviour and altered social behaviour. We repeated these behavioural tests in a second rbfox1 mutant line with a different genetic background (TU), rbfox1del19, and found that rbfox1 deficiency affects behaviour similarly in this line, although there were some differences. rbfox1del19 mutants present similar thigmotaxis, but stronger alterations in social behaviour and lower levels of hyperactivity than rbfox1sa15940 fish. Taken together, these results suggest that mutations in rbfox1 lead to multiple behavioural changes in zebrafish that might be modulated by environmental, epigenetic and genetic background effects, and that resemble phenotypic alterations present in Rbfox1-deficient mice and in patients with different psychiatric conditions. Our study, thus, highlights the evolutionary conservation of rbfox1 function in behaviour and paves the way to further investigate the mechanisms underlying rbfox1 pleiotropy on the onset of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
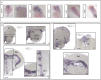
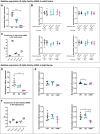

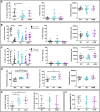
Update of
-
Pleiotropic contribution of rbfox1 to psychiatric and neurodevelopmental phenotypes in a zebrafish model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 24:2023.02.23.529711. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529711. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 19;14(1):99. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02801-6. PMID: 36865197 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Decreased Brain Serotonin in rbfox1 Mutant Zebrafish and Partial Reversion of Behavioural Alterations by the SSRI Fluoxetine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 16;17(2):254. doi: 10.3390/ph17020254. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399469 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic contribution of rbfox1 to psychiatric and neurodevelopmental phenotypes in a zebrafish model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 24:2023.02.23.529711. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529711. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 19;14(1):99. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02801-6. PMID: 36865197 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Behavioural and functional evidence revealing the role of RBFOX1 variation in multiple psychiatric disorders and traits.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Nov;27(11):4464-4473. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01722-4. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35948661 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestration of neurodevelopmental programs by RBFOX1: implications for autism spectrum disorder.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;113:251-67. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-418700-9.00008-3. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 24290388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RBFOX1, encoding a splicing regulator, is a candidate gene for aggressive behavior.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Jan;30:44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.11.012. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 29174947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased Brain Serotonin in rbfox1 Mutant Zebrafish and Partial Reversion of Behavioural Alterations by the SSRI Fluoxetine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 16;17(2):254. doi: 10.3390/ph17020254. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399469 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary neurogenomics: Lengthy resolutions for complex brains.Curr Biol. 2024 Apr 22;34(8):R315-R318. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.03.016. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38653198 Free PMC article.
-
rbfox1 loss in zebrafish drives HPI axis hyperactivation via bdnf/trkb2 pathway and allostatic overload during later life.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 11:2024.10.09.616976. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.09.616976. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39464042 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Griswold AJ, Dueker ND, Van Booven D, Rantus JA, Jaworski JM, Slifer SH, et al. Targeted massively parallel sequencing of autism spectrum disorder-associated genes in a case control cohort reveals rare loss-of-function risk variants. Mol Autism. 2015;6:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13229-015-0034-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

