Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology
- PMID: 38374256
- PMCID: PMC10937372
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07019-6
Genetic drivers of heterogeneity in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology
Abstract
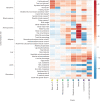
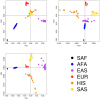
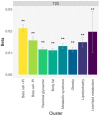
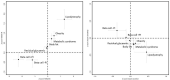
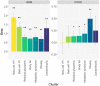
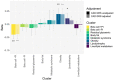
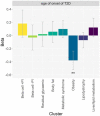
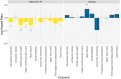
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a heterogeneous disease that develops through diverse pathophysiological processes1,2 and molecular mechanisms that are often specific to cell type3,4. Here, to characterize the genetic contribution to these processes across ancestry groups, we aggregate genome-wide association study data from 2,535,601 individuals (39.7% not of European ancestry), including 428,452 cases of T2D. We identify 1,289 independent association signals at genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10-8) that map to 611 loci, of which 145 loci are, to our knowledge, previously unreported. We define eight non-overlapping clusters of T2D signals that are characterized by distinct profiles of cardiometabolic trait associations. These clusters are differentially enriched for cell-type-specific regions of open chromatin, including pancreatic islets, adipocytes, endothelial cells and enteroendocrine cells. We build cluster-specific partitioned polygenic scores5 in a further 279,552 individuals of diverse ancestry, including 30,288 cases of T2D, and test their association with T2D-related vascular outcomes. Cluster-specific partitioned polygenic scores are associated with coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease and end-stage diabetic nephropathy across ancestry groups, highlighting the importance of obesity-related processes in the development of vascular outcomes. Our findings show the value of integrating multi-ancestry genome-wide association study data with single-cell epigenomics to disentangle the aetiological heterogeneity that drives the development and progression of T2D. This might offer a route to optimize global access to genetically informed diabetes care.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.A.S. is now an employee of GlaxoSmithKline. G.T. is an employee of deCODE Genetics (Amgen). A.S.B. reports institutional grants from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biogen, BioMarin, Bioverativ, Novartis, Regeneron and Sanofi. J. Danesh serves on scientific advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Novartis and UK Biobank, and has received multiple grants from academic, charitable and industry sources outside of the submitted work. L.S.E. is now an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. J.S.F. has consulted for Shionogi. T.M.F. has consulted for Sanofi and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has received funding from GlaxoSmithKline. H.C.G. holds the McMaster-Sanofi Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research and Care; reports research grants from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Merck, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi; reports honoraria for speaking from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, DKSH, Zuellig, Roche and Sanofi; and reports consulting fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sanofi, Kowa and Hanmi. M. Ingelsson is a paid consultant to BioArctic AB. R.L.-G. is a part-time consultant for Metabolon. A.E.L. is now an employee of Regeneron Genetics Center and holds shares in Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. M.A.N. currently serves on the scientific advisory board for Clover Therapeutics and is an advisor to Neuron23. S.R.P. has received grant funding from Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Philips Respironics and Respicardia. N. Sattar has consulted for or been on the speaker bureau for Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Hanmi, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi and Pfizer, and has received grant funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis and Roche Diagnostics. V.S. is now an employee of deCODE Genetics/Amgen Inc. A.M.S. receives funding from Seven Bridges Genomics to develop tools for the NHLBI BioData Catalyst consortium. U.T. is an employee of deCODE Genetics (Amgen). E. Ingelsson is now an employee of GlaxoSmithKline. B.M.P. serves on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. R.C.W.M. reports research funding from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Tricida and Sanofi, and has consulted for or received speaker’s fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer and Boehringer Ingelheim, all of which have been donated to the Chinese University of Hong Kong to support diabetes research. D.O.M.-K. is a part-time clinical research consultant for Metabolon. S. Liu reports consulting payments and honoraria or promises of the same for scientific presentations or reviews at numerous venues, including but not limited to Barilla, By-Health, Ausa Pharmed., Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Harvard University, University of Buffalo, Guangdong General Hospital and Academy of Medical Sciences; is a consulting member for Novo Nordisk; is a member of the Data Safety and Monitoring Board for a trial of pulmonary hypertension in patients with diabetes at Massachusetts General Hospital; receives royalties from UpToDate; and receives an honorarium from the American Society for Nutrition for his duties as Associate Editor. K. Stefansson is an employee of deCODE Genetics (Amgen). M.I.M. has served on advisory panels for Pfizer, Novo Nordisk and Zoe Global; has received honoraria from Merck, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly; has received research funding from Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi Aventis, Servier and Takeda; and is now an employee of Genentech and a holder of Roche stock. J.B.M. is an Academic Associate for Quest Diagnostics R&D. A. Mahajan is an employee of Genentech, and a holder of Roche stock. The TIMI Study Group received institutional research grants through Brigham and Women’s Hospital supported by: Abbott, Abiomed, Inc., Amgen, Anthos Therapeutics, ARCA Biopharma, Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Janssen Research and Development, LLC, Medimmune, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Roche, Saghmos Therapeutics, Inc., Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Inc. Softcell Medical Limited, The Medicines Company, Verve Therapeutics, Inc, and Zora Biosciences. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 DK126194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_14135/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- I01 BX003362/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 DK134575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK126185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078150/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U137686851/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R00 AG066849/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 DK126146/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK131249/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 212946/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL163262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD030880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 29186/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K23 DK114551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153805/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142302/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/W029626/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK105535/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG011723/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK139598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

