Regorafenib plus nivolumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: the phase 2 RENOBATE trial
- PMID: 38374347
- PMCID: PMC10957471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02824-y
Regorafenib plus nivolumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: the phase 2 RENOBATE trial
Abstract
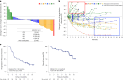
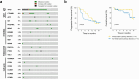
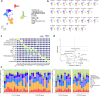
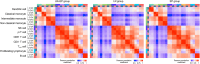
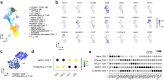
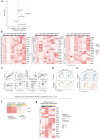
Regorafenib has anti-tumor activity in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC) with potential immunomodulatory effects, suggesting that its combination with immune checkpoint inhibitor may have clinically meaningful benefits in patients with uHCC. The multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 RENOBATE trial tested regorafenib-nivolumab as front-line treatment for uHCC. Forty-two patients received nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks and regorafenib 80 mg daily (3-weeks-on/1-week-off schedule). The primary endpoint was the investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR) per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1. The secondary endpoints included safety, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). ORR per RECIST version 1.1 was 31.0%, meeting the primary endpoint. The most common adverse events were palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (38.1%), alopecia (26.2%) and skin rash (23.8%). Median PFS was 7.38 months. The 1-year OS rate was 80.5%, and the median OS was not reached. Exploratory single-cell RNA sequencing analyses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells showed that long-term responders exhibited T cell receptor repertoire diversification, enrichment of genes representing immunotherapy responsiveness in MKI67+ proliferating CD8+ T cells and a higher probability of M1-directed monocyte polarization. Our data support further clinical development of the regorafenib-nivolumab combination as front-line treatment for uHCC and provide preliminary insights on immune biomarkers of response. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04310709 .
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.Y. received honoraria from Servier, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Eisai, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Novartis, Boryung Pharmaceuticals, Mundipharma and Roche and received research grants from Servier, Bayer, AstraZeneca, Ono Pharmaceuticals, Ipsen and Boryung Pharmaceuticals. H.-D.K. received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceuticals, Boryung Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Daehwa and Boostimmune and served as a consultant for Mustbio. H.J.C. holds consulting or advisory roles with Eisai, Roche, Bayer, Ono Pharmaceuticals, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Servier, AstraZeneca, SillaJen, Menarini and GreenCross Cell and has received research grants from Roche, Dong-A ST and Boryung Pharmaceuticals. D.T. received honoraria from Novartis, Celgene, Sirtex, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Eisai, Ipsen, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche and AstraZeneca and research support from Novartis, Sirtex and Bristol Myers Squibb. R.S.F. reports grants or contracts to institution from Adaptimmune, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Roche and Genentech; personal consulting fees from Merck, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Cstone, Hengrui, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, Roche and Genentech; personal payments or honoraria from Genentech; and participation on a data safety monitoring or advisory board for AstraZeneca and Hengrui. All other authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures






References
-
- Abou-Alfa, G. K. et al. Tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 10.1056/EVIDoa2100070 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

