FOXM1: a new therapeutic target of extramammary Paget disease
- PMID: 38374400
- PMCID: PMC10876583
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54773-8
FOXM1: a new therapeutic target of extramammary Paget disease
Abstract
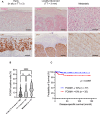
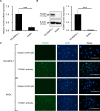
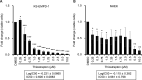
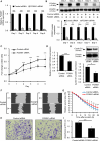
Extramammary Paget disease (EMPD) is a rare skin cancer that primarily affects older individuals predominantly in areas with apocrine sweat glands. Although most early EMPD lesions are indolent, patients with metastatic EMPD have a poor prognosis due to the lack of effective systemic treatment. In this study, we investigated the role of forkhead box M1 (FOXM1), a potent transcription factor, in EMPD and assessed the potential of FOXM1 as a therapeutic target. Immunohistochemistry of 112 primary and 17 metastatic EMPD samples revealed that FOXM1 expression increased with tumor progression. Patients in whom FOXM1 was expressed in more than 10% of tumor cells had significantly shorter disease-specific survival than the other patients (p = 0.0397). In in vitro studies using our newly established EMPD cell line, KS-EMPD-1, we found high expression of FOXM1. Knockdown of FOXM1 impaired tumor cell viability, migration, and invasion. Inhibition of FOXM1 using thiostrepton also reduced tumor cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. These findings suggest that FOXM1 is a promising therapeutic target for patients with EMPD.
Keywords: Cell line; FOXM1; Skin cancer; Targeted therapy; Thiostrepton.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multicenter study on TROP2 as a potential targeted therapy for extramammary Paget disease in Japan.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84566-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747638 Free PMC article.
-
NECTIN4-targeted antibody-drug conjugate is a potential therapeutic option for extramammary Paget disease.Exp Dermatol. 2024 Mar;33(3):e15049. doi: 10.1111/exd.15049. Exp Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38509717
-
Prognostic significance of forkhead box M1 (FoxM1) expression and antitumour effect of FoxM1 inhibition in melanoma.Histopathology. 2016 Jul;69(1):63-71. doi: 10.1111/his.12909. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Histopathology. 2016. PMID: 26619071
-
Extramammary Paget disease. Part I. epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, and diagnosis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024 Sep;91(3):409-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2023.07.1051. Epub 2024 May 2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38704032 Review.
-
Extramammary Paget's disease: a report of three cases and review of the literature.Ann Acad Med Singap. 1995 Jul;24(4):636-9. Ann Acad Med Singap. 1995. PMID: 8849202 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling ammonia-induced cell death: a new frontier in clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 31;16:1636977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1636977. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40821775 Free PMC article.
-
A multicenter study on TROP2 as a potential targeted therapy for extramammary Paget disease in Japan.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84566-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747638 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

