Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
- PMID: 38374413
- PMCID: PMC11904852
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01620-6
Chimeric nanobody-decorated liposomes by self-assembly
Abstract
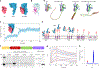
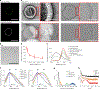
Liposomes as drug vehicles have advantages, such as payload protection, tunable carrying capacity and improved biodistribution. However, due to the dysfunction of targeting moieties and payload loss during preparation, immunoliposomes have yet to be favoured in commercial manufacturing. Here we report a chemical modification-free biophysical approach for producing immunoliposomes in one step through the self-assembly of a chimeric nanobody (cNB) into liposome bilayers. cNB consists of a nanobody against human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), a flexible peptide linker and a hydrophobic single transmembrane domain. We determined that 64% of therapeutic compounds can be encapsulated into 100-nm liposomes, and up to 2,500 cNBs can be anchored on liposomal membranes without steric hindrance under facile conditions. Subsequently, we demonstrate that drug-loaded immunoliposomes increase cytotoxicity on HER2-overexpressing cancer cell lines by 10- to 20-fold, inhibit the growth of xenograft tumours by 3.4-fold and improve survival by more than twofold.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
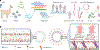
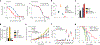
References
-
- Liu Y, Castro Bravo KM & Liu J Targeted liposomal drug delivery: a nanoscience and biophysical perspective. Nanoscale Horiz. 6, 78–94 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Pattni BS, Chupin VV & Torchilin VP New developments in liposomal drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 115, 10938–10966 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Mamot C et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted immunoliposomes significantly enhance the efficacy of multiple anticancer drugs in vivo. Cancer Res. 65, 11631–11638 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

