Deep volcanic residual U-Net for nodal metastasis (Nmet) identification from lung cancer
- PMID: 38374909
- PMCID: PMC10874362
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-023-00332-5
Deep volcanic residual U-Net for nodal metastasis (Nmet) identification from lung cancer
Abstract
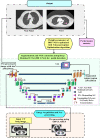
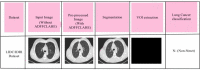
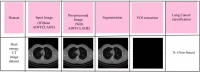
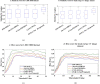
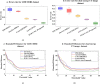
Lymph node metastasis detections are more clinically significant task associated with the presence and reappearance of lung cancer. The development of the computer-assisted diagnostic approach has greatly supported the diagnosis of human disorders in the field of medicine including lung cancer. Lung cancer treatment is possible if it is detected at the initial stage. Radiologists have great difficulty identifying and categorizing lung cancers in the initial phase. So, several methods were used to predict the lung cancer but does not provide accurate solutions with increased error rate. To overcome these issues, a Deep Volcanic Residual U-Net (DVR U-Net) for nodal metastasis is proposed in this manuscript which identifies the LC accurately in the early stage. Initially, the input images are taken from two datasets. After that, these input data are pre-processed using Anisotropic Diffusion Filter with a Fuzzy based Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (ADFFCLAHE) method. Then the pre-processed images are given to the DVR U-Net to segment and extract the volume of interest for estimating the nodal stage of each volume of interest. Finally, DVR U-Net effectively detects and classifies the N + (nodal metastasis) or N- (non-nodal metastasis). The introduced method attains 99.9% higher accuracy as compared with the existing methods. Also, the statistical analysis of the Shapiro-Wilk test, Friedman test and Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test are executed to prove the statistical effectiveness of the implemented method.
Keywords: Deep Residual U-Net; Lymph node metastasis identification; Node metastasis; Non-Node metastasis; Volcano eruption algorithm.
© Korean Society of Medical and Biological Engineering 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Kaya SI, Ozcelikay G, Mollarasouli F, Bakirhan NK, Ozkan SA. Recent achievements and challenges on nanomaterial based electrochemical biosensors for the detection of colon and lung cancer biomarkers. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2022;351:130856. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2021.130856. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
