Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Presenting as an Isolated Brain Lesion 6 Years After Treatment
- PMID: 38374924
- PMCID: PMC10876248
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001263
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Presenting as an Isolated Brain Lesion 6 Years After Treatment
Abstract
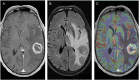
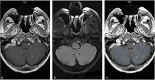
Intracranial metastasis is a rare sequela of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), typically presenting within the first 2 years after primary tumor detection. Our patient is a 72-year-old man diagnosed with an EAC in 2015 and presented with recurrence of a distant solitary brain lesion approximately 6 years after the initial diagnosis. Histological diagnosis was confirmed as EAC with all relevant indicators. In addition, we used genomic profiling to detect biomarkers that can be useful in the future for therapies.
Keywords: brain metastasis; esophageal adenocarcinoma; gamma-knife radiation; gastroenterology; immunotherapy; neurooncology; next-generation sequencing.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures


References
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64(3):381–7. - PubMed
-
- Coleman HG, Xie SH, Lagergren J. The epidemiology of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(2):390–405. - PubMed
-
- Vanstraelen S, Depypere L, Moons J, et al. . How to handle brain tumors after esophagectomy with curative intent: A single center 20-year experience. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023;49(9):106916. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

