Depression, anxiety, lower sleep quality and social support in square cabin hospitals during Shanghai's COVID-19 lockdown, China
- PMID: 38374973
- PMCID: PMC10875048
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1339774
Depression, anxiety, lower sleep quality and social support in square cabin hospitals during Shanghai's COVID-19 lockdown, China
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate and compare the associated factors of depression, anxiety, and other psychological differences between patients with Corona Virus Disease 2019 quarantined in square cabin hospitals (SCH) and isolation wards (IW) in China.
Methods: Cluster sampling method was performed during Shanghai's Two-Month Lockdown in 2022. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale Depression subscale (HADS-D), 7-tiem Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD-7), Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI), and Perceived Social Support Scale (PSSS) were used to investigate psychological differences.
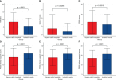
Results: The HADS-D and GAD-7 scores of SCH patients were significantly higher than those in IW (p < 0.001; p = 0.0295). Sleep latency (SCH-IW = -3.76, p < 0.001), sleep duration (SCH-IW = -2.22, p < 0.05), habitual sleep efficiency (SCH-IW = -4.11, p < 0.001), sleep disturbance (SCH-IW = -3.59, p < 0.001) and use of sleep medication (SCH-IW = -5.18, p < 0.001) of SCH patients were significantly worse. Depression was the main emotional problem of quarantined patients. Patients in SCH had lower social support. Sleep disorders and the lowest oxygen saturation ≤ 93% were risk factors for depression, while social support and child status were protective factors. Myalgia and constipation were risk factors for anxiety, while marital status was the protective factor.
Conclusion: Patients quarantined in SCH had higher risks of depression and anxiety, lower sleep quality and social support. Somatic discomfort and sleep disorders exacerbated depression and anxiety, which could be ameliorated by social support and taken into consideration in future SCH construction.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; isolation wards; sleep; social support; square cabin hospitals.
Copyright © 2024 Quan, Xu, Xu, Chen, Wu, Zhu, Liu and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep Quality and Psychosocial Factors in Liver Transplant Recipients at an Outpatient Follow-Up Clinic in China.Ann Transplant. 2020 Feb 18;25:e920984. doi: 10.12659/AOT.920984. Ann Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32066650 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic-related depression and anxiety under lockdown: The chain mediating effect of self-efficacy and perceived stress.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 26;14:1100242. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1100242. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37181887 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive muscle relaxation alleviates anxiety and improves sleep quality among healthcare practitioners in a mobile cabin hospital: a pre-post comparative study in China.Front Psychol. 2024 Apr 30;15:1337318. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1337318. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38746917 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of sleep disorders on somatic symptoms, mental health, and quality of life in patients with chronic constipation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Feb;96(7):e6093. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006093. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28207519 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of sleep disturbance and related factors in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Dec 18;52(6):1063-1068. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.06.012. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 33331314 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Social support and sleep quality in people with schizophrenia living in the community: the mediating roles of anxiety and depression symptoms.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 30;12:1414868. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1414868. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39139661 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical correlation-based relationships between social support and sleep quality in a hospital psychiatric outpatient population with examining the mediating roles of anxiety and depressive symptoms.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 7;14(1):27139. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78775-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39511319 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

