Multiple roles of baicalin and baicalein in the regulation of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38375035
- PMCID: PMC10875017
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1264418
Multiple roles of baicalin and baicalein in the regulation of colorectal cancer
Abstract
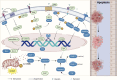
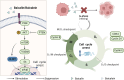
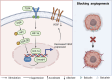
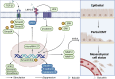
The prevalence of colorectal cancer is increasing worldwide, and despite advances in treatment, colorectal cancer (CRC) remains in the top three for mortality due to several issues, including drug resistance and low efficiency. There is increasing evidence that baicalin and baicalein, novel small molecule inhibitor extracts of the Chinese herb Scutellaria baicalensis, have better anti-colorectal cancer effects and are less likely to induce drug resistance in cancer cells. The present review article explains the anti-proliferative properties of baicalin and baicalein in the context of against CRC. Additionally, it explores the underlying mechanisms by which these compounds modulate diverse signaling pathways associated with apoptosis, cell proliferation, tumor angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and tumor microenvironment. Moreover, this review article highlights the inhibitory effect of colorectal inflammatory-cancer transformation and the near-term therapeutic strategy of using them as adjuvant agents in chemotherapy.
Keywords: apoptosis; baicalein; baicalin; colorectal cancer; signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Wu, Peng, You, Ren, Li and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
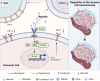
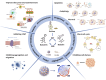
References
-
- Akao T., Kawabata K., Yanagisawa E., Ishihara K., Mizuhara Y., Wakui Y., et al. (2000). Baicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 52, 1563–1568. 10.1211/0022357001777621 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bai H. R., Sa Y. L., Lu S., Bai H. Y., Liu P. (2017). Baicalin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human colon cancer invitro and in vivo . Tumor 37, 208–217.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

