Optimal timing of GnRH antagonist initiation in IVF-ET: a retrospective cohort study on advanced maternal age women
- PMID: 38375197
- PMCID: PMC10875460
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1340230
Optimal timing of GnRH antagonist initiation in IVF-ET: a retrospective cohort study on advanced maternal age women
Abstract
Background: Several studies have compared the effects of fixed and flexible gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist (GnRH-ant) protocols during in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer (IVF-ET). However, which GnRH-ant initiation strategy is better remains controversial. Moreover, no studies have assessed the optimal timing of GnRH-ant initiation in women of advanced maternal age (AMA).
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, a total of 472 infertile women aged ≥ 35 years old undergoing their first IVF cycle from August 2015 to September 2021 at a tertiary academic medical center were recruited, of whom 136 followed fixed GnRH-ant protocol and 336 followed flexible GnRH-ant protocol. The primary outcomes measured were the cumulative live birth rate (CLBR) per IVF cycle and the time to live birth (TTLB) from the date of oocyte retrieval. Cox proportional models were used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of CLBR regarding GnRH-ant timing.
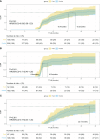
Results: No significant difference in CLBR was found between the fixed and flexible GnRH-ant groups (27.9% vs 20.5%, p=0.105). The TTLB was also comparable between groups (10.56 vs 10.30 months, p=0.782). The Kaplan-Meier analysis for CLBR also showed comparable results between groups (P=0.351, HR=0.83; 95%CI: 0.56-1.23). After establishing a multiple Cox proportional hazard model, the fixed GnRH-ant group still had comparable CLBR with the flexible GnRH-ant group (HR=0.85; 95%CI: 0.53-1.38; P=0.518). Subgroup and sensitivity analyses also demonstrated similar results.
Conclusion: GnRH-ant protocols can be tailored to the needs of AMA women, and timing of GnRH-ant initiation can be adjusted flexibly.
Keywords: Cox proportional hazard model; advanced maternal age; cumulative live birth rate; fixed GnRH-ant protocol; flexible GnRH-ant protocol.
Copyright © 2024 Han, Zhou, Xu, Ai, Song and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

