TOP1 and R-loops facilitate transcriptional DSBs at hypertranscribed cancer driver genes
- PMID: 38375218
- PMCID: PMC10875566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109082
TOP1 and R-loops facilitate transcriptional DSBs at hypertranscribed cancer driver genes
Abstract
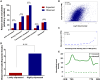
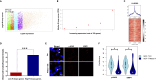
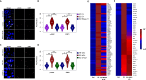
DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) pose a significant threat to genomic integrity, and their generation during essential cellular processes like transcription remains poorly understood. In this study, we employ several techniques to map DSBs, R-loops, and topoisomerase 1 cleavage complex (TOP1cc) to comprehensively investigate the interplay between transcription, DSBs, topoisomerase 1 (TOP1), and R-loops. Our findings reveal the presence of DSBs at highly expressed genes enriched with TOP1 and R-loops. Remarkably, transcription-associated DSBs at these loci are significantly reduced upon depletion of R-loops and TOP1, uncovering the pivotal roles of TOP1 and R-loops in transcriptional DSB formation. By elucidating the intricate interplay between TOP1cc trapping, R-loops, and DSBs, our study provides insights into the mechanisms underlying transcription-associated genomic instability. Moreover, we establish a link between transcriptional DSBs and early molecular changes driving cancer development, highlighting the distinct etiology and molecular characteristics of driver mutations compared to passenger mutations.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cancer; Molecular mechanism of gene regulation; Transcriptomics.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual Processing of R-Loops and Topoisomerase I Induces Transcription-Dependent DNA Double-Strand Breaks.Cell Rep. 2019 Sep 17;28(12):3167-3181.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.041. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31533039 Free PMC article.
-
Deletions associated with stabilization of the Top1 cleavage complex in yeast are products of the nonhomologous end-joining pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 5;116(45):22683-22691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914081116. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31636207 Free PMC article.
-
TDP1-independent pathways in the process and repair of TOP1-induced DNA damage.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 22;13(1):4240. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31801-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35869071 Free PMC article.
-
The distinctive cellular responses to DNA strand breaks caused by a DNA topoisomerase I poison in conjunction with DNA replication and RNA transcription.Genes Genet Syst. 2016;90(4):187-94. doi: 10.1266/ggs.15-00023. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Genes Genet Syst. 2016. PMID: 26616758 Review.
-
Relationship among DNA double-strand break (DSB), DSB repair, and transcription prevents genome instability and cancer.Cancer Sci. 2020 May;111(5):1443-1451. doi: 10.1111/cas.14404. Epub 2020 May 9. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32232911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated reactive oxygen species can drive the alternative lengthening of telomeres pathway in ATRX-null cancers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf061. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf061. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39921567 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlining R-loop biology and implications for human disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Feb 21;13:1537731. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1537731. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40061014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precise Mapping of Physiological DSBs Using In-Suspension Break Labeling In Situ and Sequencing (sBLISS).Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2906:113-136. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4426-3_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40082353
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

