Antiphotoaging effects of solvent fractions isolated from Allomyrina dichotoma larvae extract
- PMID: 38375419
- PMCID: PMC10875253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101660
Antiphotoaging effects of solvent fractions isolated from Allomyrina dichotoma larvae extract
Abstract
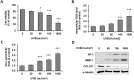
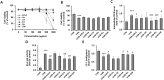
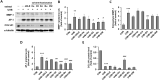
Skin aging is affected by a variety of factors, including ultraviolet rays, oxidative stress, medications, smoking, and genetics. Among them, photo-aging accounts for about 80% of skin aging. The present study was evaluated to verify the potential of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae, which has recently been attracting attention as an edible insect, as an anti-aging substance. UVB irradiation at 100 mJ/cm2 was sufficient to induce photo-aging of fibroblasts within 24 h, which was alleviated after treatment with 70% ethanol extract of Allomyrina dichotoma larvae extract (ADLE). To obtain an extract from ADLE, which has a relatively high content of polyphenol compounds containing physiological activity, fractional solvent extraction was carried out using organic solvents such as hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and butanol. Additionally, ethyl acetate and butanol fractions contributed to the inhibition of UVB-induced ROS production, cell damage, and senescence of fibroblasts. It was also confirmed that the two fractions can regulate the expression of MMP-1 and AP-1. In particular, the ethyl acetate fraction showed an excellent effect in recovering collagen decomposed by UVB. Therefore, these results suggest that ADLE has potential as a natural insect-derived biomaterial to inhibit UVB-induced photo-aging.
Keywords: Allomyrina dichotoma larvae; Collagen; Human dermal fibroblast; Photo-aging; Ultraviolet B.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of UVB-Induced Photoaging by an Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Allomyrina dichotoma Larvae and Its Potential Mechanisms in Human Dermal Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7850. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147850. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063091 Free PMC article.
-
Allomyrina dichotoma larval extract attenuates intestinal barrier disruption by altering inflammatory response and tight junction proteins in lipopolysaccharide-induced Caco-2 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Oct 29;532(1):145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.034. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32828534
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of AF-13, an Antioxidant Compound Isolated from the Polar Fraction of Allomyrina dichotoma Larva, in Palmitate-Induced INS-1 Cells.Life (Basel). 2021 May 24;11(6):470. doi: 10.3390/life11060470. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34073736 Free PMC article.
-
Allomyrina dichotoma Larva Extract Ameliorates the Hepatic Insulin Resistance of High-Fat Diet-Induced Diabetic Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 4;11(7):1522. doi: 10.3390/nu11071522. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31277481 Free PMC article.
-
Allomyrina dichotoma larva extract attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells.Nutr Res Pract. 2021 Jun;15(3):294-308. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2021.15.3.294. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Nutr Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 34093971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevention of UVB-Induced Photoaging by an Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Allomyrina dichotoma Larvae and Its Potential Mechanisms in Human Dermal Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 18;25(14):7850. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147850. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varani J., Spearman D., Perone P., Fligiel S.E., Datta S.C., Wang Z.Q., Shao Y., Kang S., Fisher G.J., Voorhees J.J. Inhibition of type I procollagen synthesis by damaged collagen in photoaged skin and by collagenase-degraded collagen in vitro. Am. J. Pathol. 2001;158:931–942. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64040-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

