IRF3 function and immunological gaps in sepsis
- PMID: 38375470
- PMCID: PMC10874998
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1336813
IRF3 function and immunological gaps in sepsis
Abstract
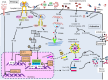
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces potent cell activation via Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation protein 2 (TLR4/MD-2), often leading to septic death and cytokine storm. TLR4 signaling is diverted to the classical acute innate immune, inflammation-driving pathway in conjunction with the classical NF-κB pivot of MyD88, leading to epigenetic linkage shifts in nuclear pro-inflammatory transcription and chromatin structure-function; in addition, TLR4 signaling to the TIR domain-containing adapter-induced IFN-β (TRIF) apparatus and to nuclear pivots that signal the association of interferons alpha and beta (IFN-α and IFN-β) with acute inflammation, often coupled with oxidants favor inhibition or resistance to tissue injury. Although the immune response to LPS, which causes sepsis, has been clarified in this manner, there are still many current gaps in sepsis immunology to reduce mortality. Recently, selective agonists and inhibitors of LPS signals have been reported, and there are scattered reports on LPS tolerance and control of sepsis development. In particular, IRF3 signaling has been reported to be involved not only in sepsis but also in increased pathogen clearance associated with changes in the gut microbiota. Here, we summarize the LPS recognition system, main findings related to the IRF3, and finally immunological gaps in sepsis.
Keywords: IRF3 signaling; MyD88-depending pathway; TLR4 signaling; lipopolysaccharide (LPS); sepsis control.
Copyright © 2024 Basak and Akashi-Takamura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein stimulates CD14-dependent Toll-like receptor 4 internalization and LPS-induced TBK1-IKKϵ-IRF3 axis activation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 29;293(26):10186-10201. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796631. Epub 2018 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29760187 Free PMC article.
-
Acrolein with an alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl group inhibits LPS-induced homodimerization of toll-like receptor 4.Mol Cells. 2008 Apr 30;25(2):253-7. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18414004
-
LPS preconditioning redirects TLR signaling following stroke: TRIF-IRF3 plays a seminal role in mediating tolerance to ischemic injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Oct 14;8:140. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-140. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21999375 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4.Immunology. 2004 Oct;113(2):153-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01976.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15379975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early innate immune responses to bacterial LPS.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Feb;44:14-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.10.005. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27842237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergy of bacteriophage depolymerase with host immunity rescues sepsis mice infected with hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae of capsule type K2.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2415945. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2415945. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39429194 Free PMC article.
-
The Cholinergic Amelioration of Sepsis-Induced Baroreflex Dysfunction and Brainstem Inflammation Is Negated by Central Adenosine A3 Receptors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 9;18(3):388. doi: 10.3390/ph18030388. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143165 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback loop centered on MAF1 reduces blood-brain barrier damage in sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jan 20;30(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00686-x. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 39833662 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the genetic association between rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of infectious diseases.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):2611-2619. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07485-x. Epub 2025 May 16. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40377766
-
A Quinoxaline Derivative as a New Therapeutic Agent for Sepsis through Suppression of TLR4 Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2025 Apr 26. doi: 10.1007/s10753-025-02292-7. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 40285839
References
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. . Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest (1992) 101:1644–55. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Au WC, Moore PA, Lowther W, Juang YT, Pitha. PM. Identification of a member of the interferon regulatory factor family that binds to the interferon-stimulated response element and activates expression of interferoninduced genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (1995) 92:11657–61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.25.11657 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

