Transcriptional regulation of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 by SP1
- PMID: 38375778
- PMCID: PMC10878691
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.85985
Transcriptional regulation of SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 by SP1
Abstract
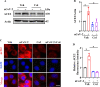
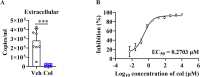
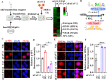
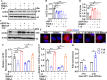
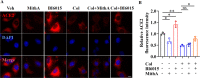
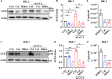
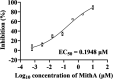
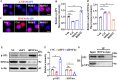
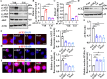
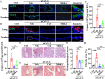
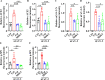
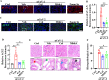
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a major cell entry receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The induction of ACE2 expression may serve as a strategy by SARS-CoV-2 to facilitate its propagation. However, the regulatory mechanisms of ACE2 expression after viral infection remain largely unknown. Using 45 different luciferase reporters, the transcription factors SP1 and HNF4α were found to positively and negatively regulate ACE2 expression, respectively, at the transcriptional level in human lung epithelial cells (HPAEpiCs). SARS-CoV-2 infection increased the transcriptional activity of SP1 while inhibiting that of HNF4α. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, activated by SARS-CoV-2 infection, served as a crucial regulatory node, inducing ACE2 expression by enhancing SP1 phosphorylation-a marker of its activity-and reducing the nuclear localization of HNF4α. However, colchicine treatment inhibited the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby suppressing ACE2 expression. In Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) infected with SARS-CoV-2, inhibition of SP1 by either mithramycin A or colchicine resulted in reduced viral replication and tissue injury. In summary, our study uncovers a novel function of SP1 in the regulation of ACE2 expression and identifies SP1 as a potential target to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-CoV-2; Sp1; infectious disease; microbiology; viruses.
© 2024, Han, Luo, Long et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HH, RL, XL, LW, QZ, XT, RZ, YM, YZ, CZ No competing interests declared
Figures



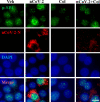
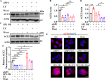
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.02.14.528496
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Replication Induces ACE2 Expression and Enhances SARS-CoV-2 Pseudotyped Virus Entry in Epithelial Cells.J Virol. 2021 Jun 10;95(13):e0019221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00192-21. Epub 2021 Jun 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33853968 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing host cellular receptor-angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression by coronavirus may facilitate 2019-nCoV (or SARS-CoV-2) infection.J Med Virol. 2020 Nov;92(11):2693-2701. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26139. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32497323 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Causes Lung Infection without Severe Disease in Human ACE2 Knock-In Mice.J Virol. 2022 Jan 12;96(1):e0151121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01511-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34668780 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) in the Pathogenesis of ARDS in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:732690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732690. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors regulating dynamics of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), the gateway of SARS-CoV-2: Epigenetic modifications and therapeutic interventions by epidrugs.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;143:112095. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112095. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34479017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemoproteomics of Marine Natural Product Naamidine J Unveils CSE1L as a Therapeutic Target in Acute Lung Injury.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Oct 16;146(41):28384-28397. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c09695. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 39324953 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurological Implications of COVID-19: A Comprehensive Narrative Review.Cureus. 2024 May 15;16(5):e60376. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60376. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38887342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of TRAF1 induced by USP7/SP1 exacerbates the severity of infantile pneumonia.Hereditas. 2025 Mar 22;162(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00410-x. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40121492 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein and ACE2 Markers in Testicular Tumors Diagnosed During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;19:11795549251347339. doi: 10.1177/11795549251347339. eCollection 2025. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40535841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brevini T, Maes M, Webb GJ, John BV, Fuchs CD, Buescher G, Wang L, Griffiths C, Brown ML, Scott WE, Pereyra-Gerber P, Gelson WTH, Brown S, Dillon S, Muraro D, Sharp J, Neary M, Box H, Tatham L, Stewart J, Curley P, Pertinez H, Forrest S, Mlcochova P, Varankar SS, Darvish-Damavandi M, Mulcahy VL, Kuc RE, Williams TL, Heslop JA, Rossetti D, Tysoe OC, Galanakis V, Vila-Gonzalez M, Crozier TWM, Bargehr J, Sinha S, Upponi SS, Fear C, Swift L, Saeb-Parsy K, Davies SE, Wester A, Hagström H, Melum E, Clements D, Humphreys P, Herriott J, Kijak E, Cox H, Bramwell C, Valentijn A, Illingworth CJR, UK-PBC Consortium. Dahman B, Bastaich DR, Ferreira RD, Marjot T, Barnes E, Moon AM, Barritt AS, Gupta RK, Baker S, Davenport AP, Corbett G, Gorgoulis VG, Buczacki SJA, Lee JH, Matheson NJ, Trauner M, Fisher AJ, Gibbs P, Butler AJ, Watson CJE, Mells GF, Dougan G, Owen A, Lohse AW, Vallier L, Sampaziotis F. FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2. Nature. 2023;615:134–142. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Callahan V, Hawks S, Crawford MA, Lehman CW, Morrison HA, Ivester HM, Akhrymuk I, Boghdeh N, Flor R, Finkielstein CV, Allen IC, Weger-Lucarelli J, Duggal N, Hughes MA, Kehn-Hall K. The Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 Are Upregulated Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection in an AKT-Dependent Manner. Viruses. 2021;13:1062. doi: 10.3390/v13061062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan JF-W, Zhang AJ, Yuan S, Poon VK-M, Chan CC-S, Lee AC-Y, Chan W-M, Fan Z, Tsoi H-W, Wen L, Liang R, Cao J, Chen Y, Tang K, Luo C, Cai J-P, Kok K-H, Chu H, Chan K-H, Sridhar S, Chen Z, Chen H, To KK-W, Yuen K-Y. Simulation of the Clinical and Pathological Manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Golden Syrian Hamster Model: Implications for Disease Pathogenesis and Transmissibility. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020;71:2428–2446. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa325. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFC2301303/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022YFC2303700/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 202103AC100005/Yunnan Key Research and Development Program
- 202103AQ100001/Yunnan Key Research and Development Program
- 202102AA310055/Yunnan Key Research and Development Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

