Rituximab treatment in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 38375947
- PMCID: PMC11235651
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.16228
Rituximab treatment in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is frequently used off-label in multiple sclerosis. However, studies on the risk-benefit profile of RTX in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis are scarce.
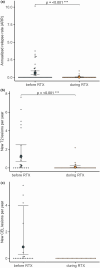
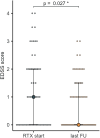
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective cohort study, patients with pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis from Sweden, Austria and Germany, who received RTX treatment were identified by chart review. Annualized relapse rates, Expanded Disability Status Scale scores and magnetic resonance imaging parameters (new T2 lesions and contrast-enhancing lesions) were assessed before and during RTX treatment. The proportion of patients who remained free from clinical and disease activity (NEDA-3) during RTX treatment was calculated. Side effects such as infusion-related reactions, infections and laboratory abnormalities were assessed.
Results: Sixty-one patients received RTX during a median (interquartile range) follow-up period of 20.9 (35.6) months. The annualized relapse rate decreased from 0.6 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.38-0.92) to 0.03 (95% CI 0.02-0.14). The annual rate of new T2 lesions decreased from 1.25 (95% CI 0.70-2.48) to 0.08 (95% CI 0.03-0.25) and annual rates of new contrast-enhancing lesions decreased from 0.86 (95% CI 0.30-3.96) to 0. Overall, 70% of patients displayed no evidence of disease activity (NEDA-3). Adverse events were observed in 67% of patients. Six patients discontinued treatment due to ongoing disease activity or adverse events.
Conclusion: Our study provides class IV evidence that RTX reduces clinical and radiological activity in pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: central nervous system; cohort study; disease‐modifying therapy; pediatric‐onset multiple sclerosis; rituximab.
© 2024 The Authors. European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
MB received speaker honoraria from Sanofi‐Genzyme. JoS received institutional consultancy fees from Mabion SA. KF received lecture honoraria from Merck; has served on scientific advisory boards for Biogen, Novartis, Merck, Roche and Celgene. JL received lecture honoraria from Biogen, Novartis, Merck, Roche, Axelion, Sanofi, Celgene and BMS; has served on scientific advisory boards for Almirall, Biogen, Novartis, Merck, Roche, Celgene, BMS and Sanofi; serves on the editorial board of the
Figures
References
-
- Chitnis T. Pediatric central nervous system demyelination. Continuum. 2019;25:793‐814. - PubMed
-
- Gorman MP, Healy BC, Polgar‐Turcsanyi M, Chitnis T. Increased relapse rate in pediatric‐onset compared with adult‐onset multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:54‐59. - PubMed
-
- Renoux C, Vukusic S, Mikaeloff Y, et al. Natural history of multiple sclerosis with childhood onset. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2603‐2613. - PubMed
-
- Ruano L, Branco M, Portaccio E, et al. Patients with paediatric‐onset multiple sclerosis are at higher risk of cognitive impairment in adulthood: an Italian collaborative study. Mult Scler. 2018;24:1234‐1242. - PubMed
-
- Bartels F, Nobis K, Cooper G, et al. Childhood multiple sclerosis is associated with reduced brain volumes at first clinical presentation and brain growth failure. Mult Scler. 2019;25:927‐936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

