ER stress and unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling modulate GLP-1 receptor signaling in the pancreatic islets
- PMID: 38376482
- PMCID: PMC10880082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mocell.2023.12.002
ER stress and unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling modulate GLP-1 receptor signaling in the pancreatic islets
Abstract
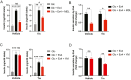
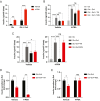
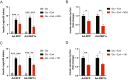
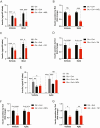
Insulin is essential for maintaining normoglycemia and is predominantly secreted in response to glucose stimulation by β-cells. Incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, also stimulate insulin secretion. However, as obesity and type 2 diabetes worsen, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide loses its insulinotropic efficacy, whereas GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists continue to be effective owing to its signaling switch from Gs to Gq. Herein, we demonstrated that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induced a transition from Gs to Gq in GLP-1R signaling in mouse islets. Intriguingly, chemical chaperones known to alleviate ER stress, such as 4-PBA and TUDCA, enforced GLP-1R's Gq utilization rather than reversing GLP-1R's signaling switch induced by ER stress or obese and diabetic conditions. In addition, the activation of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) or activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), 2 key ER stress-associated signaling (unfolded protein response) factors, promoted Gs utilization in GLP-1R signaling, whereas Gq employment by ER stress was unaffected by XBP1 or ATF6 activation. Our study revealed that ER stress and its associated signaling events alter GLP-1R's signaling, which can be used in type 2 diabetes treatment.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; G protein-coupled receptor signaling; Glucagon-like peptide-1; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interests No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced expression of ERp46 under diabetic conditions in β-cells and the effect of liraglutide.Metabolism. 2016 Jan;65(1):7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.09.011. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 26683792
-
Positive Allosteric Modulation of the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor by Diverse Electrophiles.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 13;291(20):10700-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.696039. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26975372 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells - A review of receptor interactions and co-stimulation.Peptides. 2022 May;151:170749. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 35065096 Review.
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
-
Enhanced glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide secretion and insulinotropic action in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor -/- mice.Diabetes. 1998 Jul;47(7):1046-52. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.47.7.1046. Diabetes. 1998. PMID: 9648827
Cited by
-
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot regulates cell proliferation and differentiation by endoplasmic reticulum stress.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024 Oct 2;28(1):481-494. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2024.2409452. eCollection 2024. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39364144 Free PMC article.
-
Brief guide to assays for measuring health parameters using Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cells. 2025 Aug;48(8):100233. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2025.100233. Epub 2025 May 26. Mol Cells. 2025. PMID: 40436147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of gut hormones.Mol Cells. 2024 Nov;47(11):100126. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100126. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 39426686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brief guide to Caenorhabditis elegans imaging and quantification.Mol Cells. 2025 Sep;48(9):100249. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2025.100249. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Mol Cells. 2025. PMID: 40592421 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 as an injury-responsive protein in the mouse sciatic nerve.Mol Cells. 2024 Dec;47(12):100159. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100159. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 39577744 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahren B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes (Reprinted from Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, vol 8, pg 369-385, 2009) Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2009;8:679. - PubMed
-
- Baggio L.L., Drucker D.J. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2131–2157. - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Magliano D.J., Zimmet P.Z. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus--present and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011;8:228–236. - PubMed
-
- Cross B.C., Bond P.J., Sadowski P.G., Jha B.K., Zak J., Goodman J.M., Silverman R.H., Neubert T.A., Baxendale I.R., Ron D., et al. The molecular basis for selective inhibition of unconventional mRNA splicing by an IRE1-binding small molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012;109:E869–E878. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

